Amidst escalating local weather change considerations, the Division of Power (DOE) is spearheading initiatives to speed up the deployment of carbon dioxide removing applied sciences.
For the primary time, the Division is buying $35 million in carbon removing credit by its Carbon Dioxide Removal Purchase program and Google is the primary firm to reply the decision, matching DOE’s $35 million dedication.
Carbon Clearinghouse: DOE’s Daring Transfer
The Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Change’s (IPCC) report advised that eventualities that restrict warming to 1.5°C embrace scaling carbon dioxide removing strategies to billions of tons of removing yearly over the approaching many years. Nonetheless, the report additionally highlighted that the majority current removing options are of their early phases and at present restricted in scale.
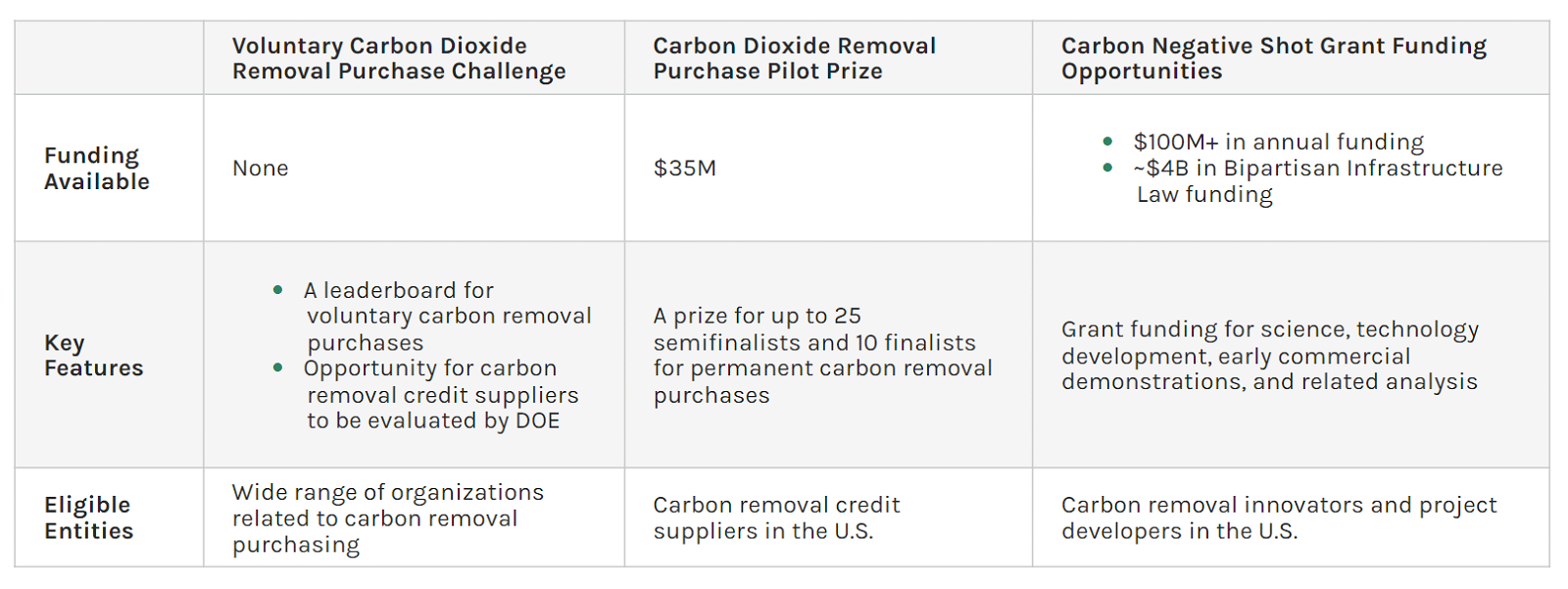
To assist scale the trade, the Division of Power (DOE) launched the Carbon Unfavorable Shot in 2021. This initiative goals to assist innovation in several CO2 removing pathways. These embrace Direct Air Capture (DAC), soil carbon sequestration, ocean-based CO2 removal, and reforestation, amongst others.
The direct air seize sector witnessed notable developments lately. These embrace latest CarbonCapture’s profitable elevate of $80 million in Sequence A funding and Climeworks unveiling its US headquarters in Austin, Texas.
The Division’s objective is to allow carbon seize and storage at gigaton scales for lower than $100 per internet metric ton of CO2e by 2032. In September 2023, the DOE introduced the Carbon Dioxide Elimination Buy Pilot Prize. This effort makes $35 million in funding obtainable to purchase carbon removal credits to assist business carbon dioxide removing corporations.
Corporations and collectives have invested billions in carbon removing, benefiting the trade considerably. This pattern highlights the significance of integrating carbon removing into local weather methods, serving as a backup for residual emissions.
As extra organizations decide to net zero targets, carbon removing turns into essential. With technological developments, carbon removing tasks are extra accessible and verifiable.
Nonetheless, future provide limitations might pose challenges for late adopters. And this main problem stays: easy methods to encourage extra organizations to begin shopping for voluntary carbon removing credit.
DOE’s Marketing campaign Fuels Carbon Seize
Increasing the funding to different corporations and organizations, the DOE introduced the Voluntary Carbon Dioxide Removal Purchasing Challenge. This initiative calls on organizations to make public bigger and bolder buy commitments just like the DOE’s $35 million carbon removing buy pilot.
However not like the Pilot Prize, the Problem doesn’t entail further federal funds.
As a part of the problem, the DOE will create a public leaderboard recognizing consumers and monitoring voluntary carbon removing purchases. It addresses non-financial obstacles similar to market transparency and recognition of the significance of carbon removing credit. Thus, the Problem seeks to foster better participation in carbon removing efforts.
How the Problem Suits into DOE Carbon Elimination Applications
The DOE is offering supporting supplies for consumers to make bigger carbon removing purchases whereas aiding CDR credit suppliers find extra prospects.
Moreover, the DOE has been actively concerned in establishing DAC hubs in Texas and Louisiana. The Texas DAC Hub is spearheaded by Occidental subsidiary 1PointFive in collaboration with companions Worley and Carbon Engineering. In the meantime, the Louisiana undertaking, named Undertaking Cypress, is led by the non-profit group Battelle, alongside expertise builders Climeworks and Heirloom.
Google Leads the Cost
Google is the primary firm to affix the DOE’s problem, matching the Division’s $35 million dedication.
By its initiatives, Google intends to contract for a minimum of $35 million price of carbon removing credit over the subsequent 12 months.
This mannequin of mutually reinforcing public-private assist is a vital software for commercializing carbon removing options. Like many rising applied sciences, governments and corporations have important and complementary roles in demonstrating promising carbon removing approaches and scaling them commercially.
Randy Spock, Google’s Carbon Credit and Removals Lead, famous that:
“We’re working hard to reduce our own emissions across our operations and value chain, but we know that tackling global climate change will require a diverse set of tools to both reduce emissions and remove them from the atmosphere.”
Spock additional highlighted that deploying CDR to deal with hard-to-abate residual emissions is essential to reaching net zero emissions.
This CDR effort builds on Google’s latest purchases by Frontier, a pioneer advance market dedication to scale breakthrough CDR approaches. The tech big can also be part of the First Movers Coalition, a world initiative of corporations collaborating to sign demand for rising local weather applied sciences.
Google’s resolution to affix the problem and commit to buying carbon removing credit prematurely has sparked anticipation that different tech giants might do the identical. Corporations like Amazon and Microsoft have already been actively buying such carbon credit immediately from issuing corporations all through 2023.
The Division of Power plans to focus on comparable bulletins going ahead, hoping “to unlock game-changing capital for high-quality and affordable CDR in time to meet our climate goals.”