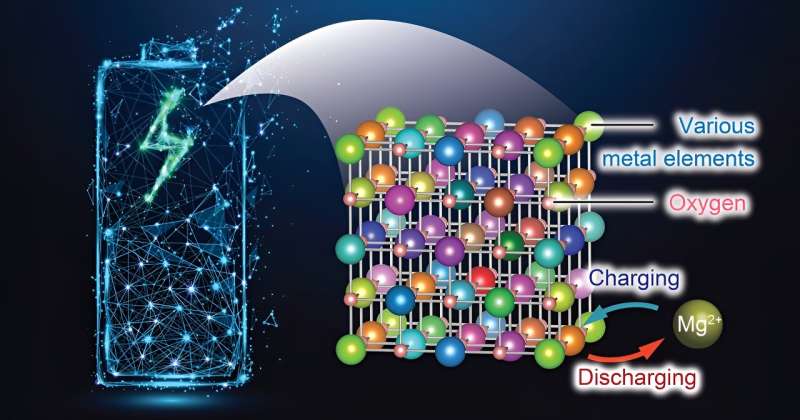
Schematics of the battery and current cathode materials. The current materials incorporates many steel parts as cations due to the impact of the excessive configurational entropy. Credit score: Tohoku College
Researchers at Tohoku College have made a development in battery know-how by creating a novel cathode materials for rechargeable magnesium batteries (RMBs) that allows environment friendly charging and discharging even at low temperatures. This modern materials, leveraging an enhanced rock-salt construction, guarantees to usher in a brand new period of vitality storage options which are extra reasonably priced, safer, and better in capability.
Details of the findings have been revealed within the Journal of Supplies Chemistry A.
The research showcases a substantial enchancment in magnesium (Mg) diffusion inside a rock-salt construction, a vital development for the reason that denseness of atoms on this configuration had beforehand impeded Mg migration. By introducing a strategic combination of seven totally different metallic parts, the analysis crew created a crystal structure ample in secure cation vacancies, facilitating simpler Mg insertion and extraction.
This represents the primary utilization of rocksalt oxide as a cathode materials for RMBs. The high-entropy technique employed by the researchers allowed the cation defects to activate the rocksalt oxide cathode.
The event additionally addresses a key limitation of RMBs—the issue of Mg transport inside solid materials. Till now, excessive temperatures have been vital to boost Mg mobility in standard cathode supplies, resembling these with a spinel construction. Nevertheless, the fabric unveiled by Tohoku College researchers operates effectively at simply 90°C, demonstrating a major discount within the required working temperature.
Tomoya Kawaguchi, a professor at Tohoku College’s Institute for Supplies Analysis (IMR), notes the broader implications of the research. “Lithium is scarce and unevenly distributed, whereas magnesium is abundantly available, offering a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative for lithium-ion batteries.”
“Magnesium batteries, that includes the newly developed cathode materialare poised to play a pivotal position in numerous functions, together with grid storage, electric vehiclesand portable electronic devices, contributing to the global shift towards renewable energy and reduced carbon footprints.”
Kawaguchi collaborated with Tetsu Ichitsubo, additionally a professor at IMR, who says, “By harnessing the intrinsic benefits of magnesium and overcoming previous material limitations, this research paves the way for the next generation of batteries, promising significant impacts on technology, the environment, and society.”
Finally, the breakthrough is a serious step ahead within the quest for environment friendly, eco-friendly vitality storage options.
Extra info:
Tomoya Kawaguchi et al, Securing cation vacancies to allow reversible Mg insertion/extraction in rocksalt oxides, Journal of Supplies Chemistry A (2024). DOI: 10.1039/D3TA07942B
Offered by
Tohoku University
Quotation:
Unleashing disordered rocksalt oxides as cathodes for rechargeable magnesium batteries (2024, March 29)
retrieved 31 March 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-03-unleashing-disordered-rocksalt-oxides-cathodes.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.