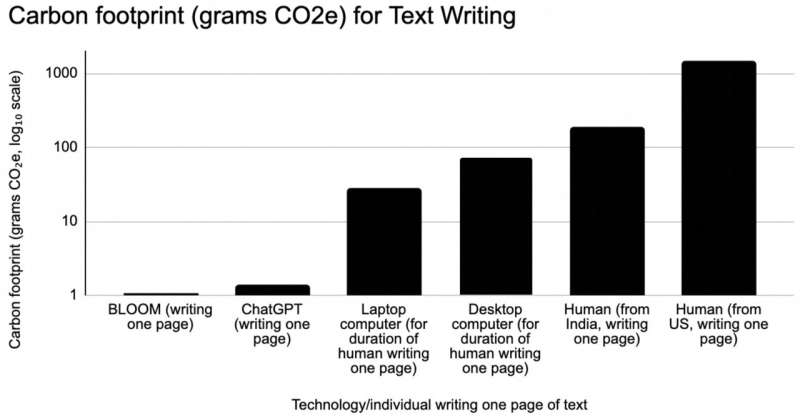
This determine compares the CO2e emissions of AI and people engaged within the process of writing one web page of textual content. AI writing (by way of BLOOM or ChatGPT) produces 130–1500 instances much less CO2e per web page than a human writer. AI additionally produces considerably much less CO2e than the pc utilization to assist people doing that writing. Credit score: Scientific Studies (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-54271-x
With the evolution of synthetic intelligence comes a dialogue of the know-how’s environmental affect. A examine has discovered that for the duties of writing and illustrating, AI emits tons of of instances much less carbon than people performing the identical duties. That doesn’t imply, nonetheless, that AI can or ought to exchange human writers and illustrators, the examine’s authors argue.
Andrew Torrance, Paul E. Wilson Distinguished Professor of Legislation at KU, is co-author of a examine that in contrast established programs reminiscent of ChatGPT, Bloom AI, DALL-E2, and others finishing writing and illustrating to that of people.
Like cryptocurrency, AI has been topic to debate in regards to the quantity of power it makes use of and its contributions to local weather change. Human emissions and environmental impact have lengthy been studied, however comparisons between the 2 have been scant. The authors performed a comparability and located that AI programs emit between 130 and 1,500 instances much less CO2e (carbon dioxide equal) per web page of textual content generated than human writers and illustration programs between 310 and a couple of,900 instances much less CO2e per picture than people.
“I like to think of myself as driven by data, not just what I feel is true. We’ve had discussions about something that appears to be true in terms of AI emissions, but we wanted to look at the data and see if it truly is more efficient,” Torrance mentioned. “When we did it, the results were kind of astonishing. Even by conservative estimates, AI is extremely less wasteful.”
The examine, co-written with Invoice Tomlinson, Rebecca Black and Donald Patterson of the College of California-Irvine, was published within the journal Scientific Studies.
To calculate the carbon footprint of an individual writing, the researchers consulted the Vitality Funds, a measure that considers the quantity of power utilized in sure duties for a set time frame.
For instance, it’s properly established how a lot power a pc with phrase processing software program makes use of per hour. When multiplied by the common time it takes an individual to write down a web page of textual content, on common, 250 phrases, an estimate will be arrived at. Utilizing the identical quantity of power utilized by the CPUs that function AI, reminiscent of ChatGPT, which may produce textual content a lot sooner, produces an estimate for AI.
Researchers additionally thought of the per capita emissions of people in the USA and India. Residents of the previous have approximate annual emissions of 15 metric tons CO2e per 12 months, whereas the latter is a median of 1.9 metric tons.
The 2 nations have been chosen as they’ve the best and lowest respective per capita environmental affect of nations with populations greater than 300 million and to supply a take a look at completely different ranges of emissions in numerous elements of the world compared to AI.
Outcomes confirmed that Bloom is 1,400 instances much less impactful than a U.S. resident writing a web page of textual content and 180 instances much less impactful than a resident of India.
By way of illustration, outcomes confirmed that DALL-E2 emits roughly 2,500 instances much less CO2e than a human artist and 310 instances lower than an India-based artist. Figures for Midjourney have been 2,900 instances much less for the previous and 370 instances much less for the latter.
As applied sciences enhance and societies evolve, these figures are nearly sure to vary as properly, Torrance mentioned.
The authors wrote that carbon emissions are just one issue to contemplate when evaluating AI manufacturing to human output. Because the applied sciences exist now, they’re typically not able to producing the standard of writing or artwork {that a} human can. As they enhance, they maintain the potential to each get rid of current jobs and create new ones.
Lack of employment has the potential for substantial financial, societal, and different types of destabilization. For these and different causes, the authors wrote, the most effective path ahead is probably going a collaboration between AI and human efforts or a system wherein folks can use AI to be extra environment friendly of their work and retain management of ultimate merchandise.
Authorized points reminiscent of using copyrighted materials in coaching units for AI have to be thought of, the authors wrote, as does the potential for a rise in artificially produced materials to lead to a rise within the power it makes use of and ensuing emissions. Collaboration between the 2 is probably the most useful use of each AI and human labor, the authors wrote.
“We don’t say AI is inherently good or that it is empirically better, just that when we looked at it in these instances, it was less energy consumptive,” Torrance mentioned.
The analysis was performed to enhance understanding of AI and its environmental affect and to deal with the United Nations Sustainable Growth Targets of guaranteeing sustainable consumption and manufacturing patterns and taking pressing motion to fight climate change and its impacts, the researchers wrote.
For his or her half, the authors have begun to make use of AI as an support in producing drafts for a few of their writing, however additionally they agree on the need of cautious modifying and including to such drafts manually.
“This is not a curse; it’s a boon,” Torrance mentioned of AI. “I think this will help make good writers great, mediocre writers good, and democratize writing. It can make people more productive and can be an empowerment of human potential. I’m hugely optimistic that technology is getting better in most respects and lightening the effects we have on the Earth. We hope this is just the beginning and that people continue to dig into this issue further.”
Extra info:
Invoice Tomlinson et al, The carbon emissions of writing and illustrating are decrease for AI than for people, Scientific Studies (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-54271-x
Offered by
University of Kansas
Quotation:
Research: AI writing, illustration emits tons of of instances much less carbon than people (2024, April 2)
retrieved 8 April 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-04-ai-emits-hundreds-carbon-humans.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.