Decarbonization efforts, aiming for Internet Zero emissions, require important adjustments within the power sector. This transition requires shifting from fossil fuels to metals and demanding minerals like cobalt, copper, lithium, nickel, and uncommon earths.
The critical minerals market will develop 7-fold by 2030, and 10-fold by 2050 to over $400 billion, per the Worldwide Vitality Company estimates. Cobalt, specifically, has a central function in reaching the worldwide internet zero goal.
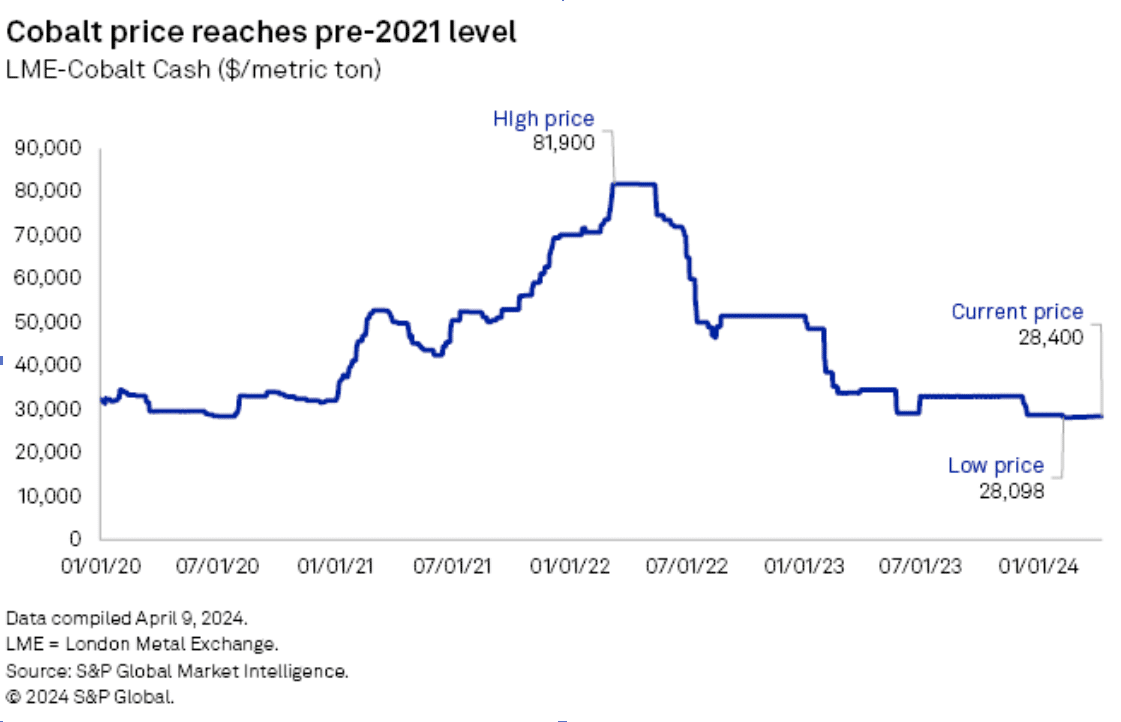
Cobalt costs have plummeted to pre-2021 ranges because the starting of the yr, with analysts predicting a continued decline. As of April 8, the London Steel Alternate cobalt money value stands at $28,400 per metric ton, marking a 65.3% drop from the 2022 excessive of $81,900/t in March,
This decline is attributed to the shortage of anticipated demand from the electrical car sector, which has additionally affected demand development in aerospace and shopper electronics.
The oversupply of cobalt out there is exacerbated by elevated output from producers in Indonesia and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Chinese language manufacturing has additionally surged, additional pressuring costs. Forecasts point out that the cobalt market will stay oversupplied by 4,000 metric tons this yr and within the forthcoming years.
Balancing Provide and Demand
Regardless of the value response to extra cobalt, producers are unlikely to chop output considerably. Cobalt manufacturing is tied to the dynamics and manufacturing prices of the copper and nickel industries, each of which proceed to see strong output. Whereas some high-cost cobalt producers could cut back output, low-cost producers are increasing manufacturing.
The IEA predicts a considerable enhance in cobalt demand, with development projected to be 5x increased between 2020 and 2040 below its Sustainable Development Scenario.
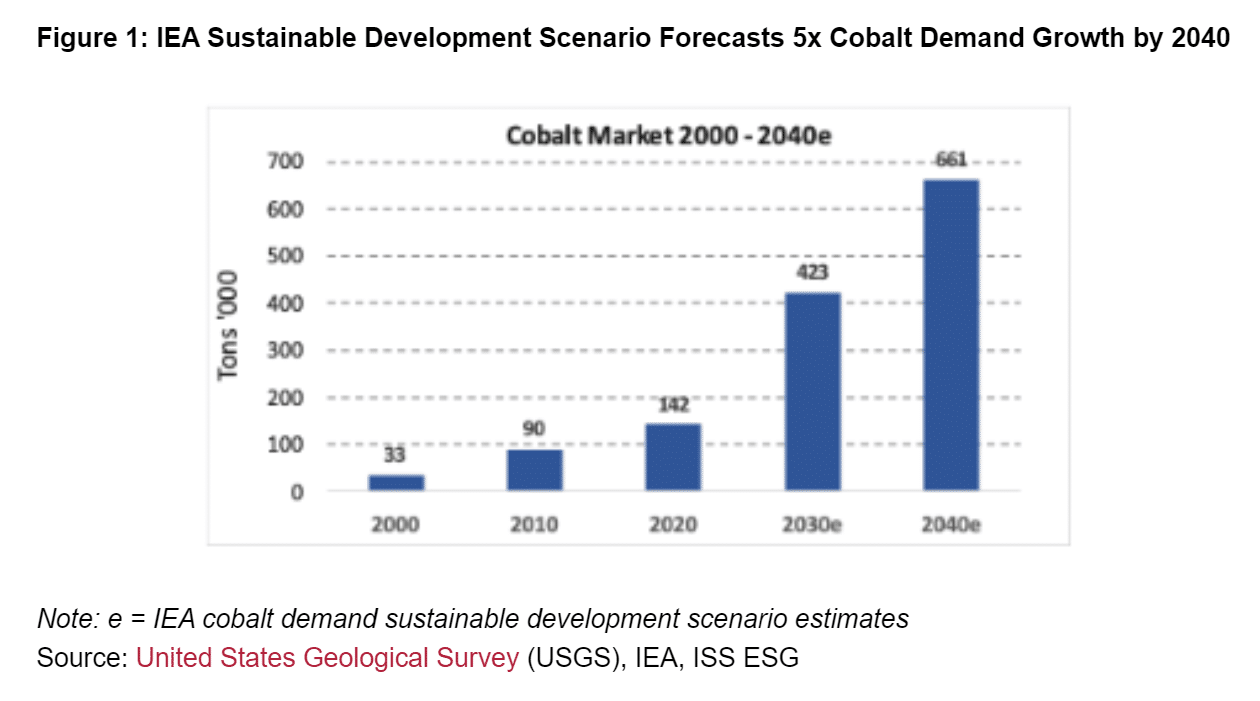 The anticipated dramatic development in cobalt demand underscores the necessity for elevated manufacturing, with the IEA forecasting a 3-fold enhance by 2030. This development trajectory requires the event of recent mines and deposits to fulfill sustainability objectives and mitigate provide dangers.
The anticipated dramatic development in cobalt demand underscores the necessity for elevated manufacturing, with the IEA forecasting a 3-fold enhance by 2030. This development trajectory requires the event of recent mines and deposits to fulfill sustainability objectives and mitigate provide dangers.
The company additionally predicts that as early as 2030, mines will produce solely 50% of the cobalt and lithium and 80% of copper required for the power transition.
The Excessive Stakes of Cobalt Mining
The strain on the cobalt provide chain is already evident. That is particularly contemplating that the Democratic Republic of Congo provides about 70% of the world’s cobalt. This raises issues about reliance on a single supply with questionable environmental, social, and governance (ESG) credentials.
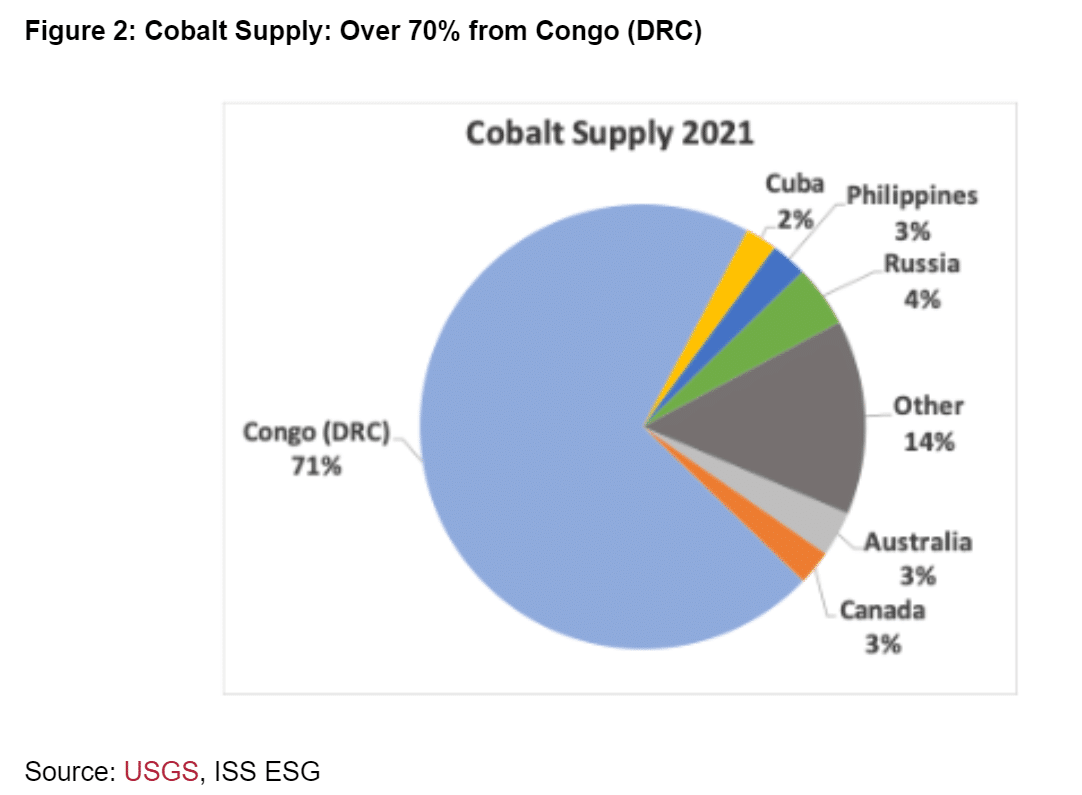
This heavy reliance on a single supply additionally poses important provide chain dangers, as evidenced by current challenges within the European pure gasoline market.
Other than provide focus, cobalt mining practices and associated points within the DRC elevate issues for buyers. These embody environmental degradation, human rights violations, and governance challenges. Consequently, buyers are more and more looking for different cobalt sources that provide better transparency and sustainability.
The cobalt mining trade additionally reveals a level of focus, with the highest 4 mining corporations contributing over 40% of worldwide manufacturing. Glencore, a diversified mining and buying and selling firm, stands out as the biggest producer, accounting for over 15% of whole manufacturing. Curiously, many of those main mining corporations are positioned in rising markets.
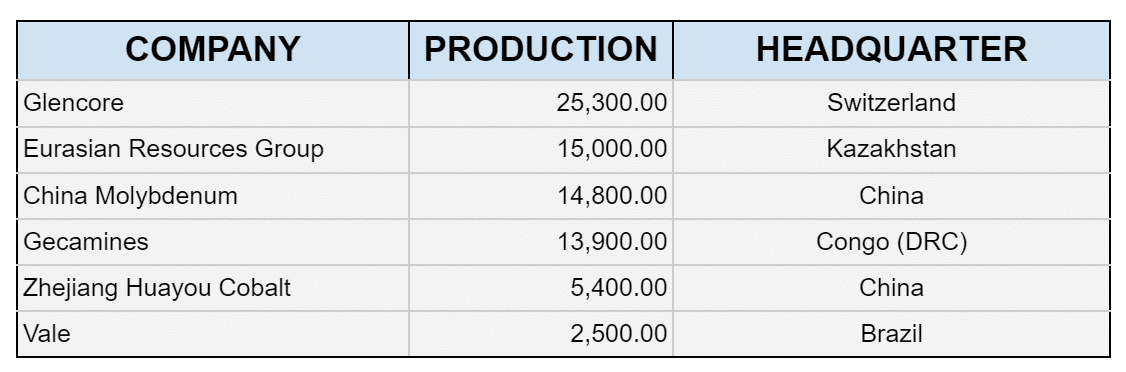
Nevertheless, there are challenges related to assessing the ESG efficiency of those corporations, significantly these which are privately held. Vale, regardless of having the bottom cobalt manufacturing among the many high 5 corporations, boasts the very best ESG score of C+.
Australia and Canada are notable for his or her substantial cobalt reserves of crucial minerals and comparatively sturdy ESG ratings. These nations supply alternatives to diversify the worldwide manufacturing mixture of crucial minerals.
Whereas the DRC stays a dominant cobalt provider, there are different sources obtainable, though they will not be as plentiful. Exploring these different provide choices is essential for mitigating provide chain dangers and making certain accountable cobalt sourcing practices.
Investing in Cobalt for a Greener Future
In response to the dangers posed by focus and ESG issues in cobalt manufacturing, stakeholders, together with buyers and energetic asset house owners, can play a major function. They’ll advocate for better transparency throughout the cobalt provide chain, incentivize sustainable practices by means of capital allocation, and have interaction with corporations to enhance their ESG efficiency.
Moreover, buyers could discover alternatives to assist tasks in jurisdictions with stronger regulatory frameworks and environmental protections. There are instruments obtainable to help buyers in navigating these challenges and pursuing accountable funding alternatives.
Though the underside for cobalt costs is unsure, some analysts anticipate a gradual enchancment in costs over the following few quarters. Nevertheless, the market stays unstable, and the trajectory of cobalt costs will rely upon numerous elements. These significantly embody demand traits and manufacturing dynamics in associated industries.
In abstract, because the world strikes in direction of Net Zero emissionsthe crucial function of cobalt within the power transition highlights the significance of sustainable and diversified provide chains to fulfill growing demand whereas addressing ESG issues.