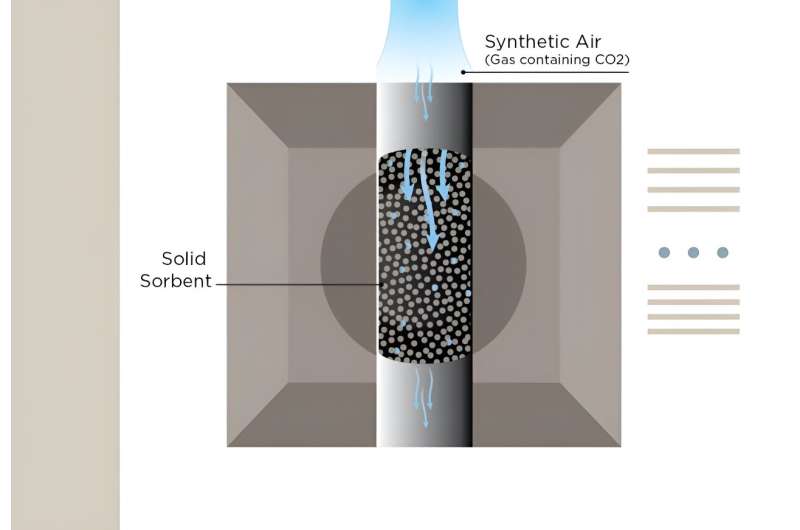
In a brand new carbon seize testing equipment, artificial air flows by a column. The sorbent traps and captures the carbon molecules. The system measures how briskly the sorbent turns into saturated with CO2. Credit score: N. Hanacek/NIST
Greater than 100 services designed to take away carbon dioxide (CO2) from the environment are in numerous levels of growth all over the world. In the USA, the primary direct air seize (DAC) plant opened final fall in Northern California. The U.S. Division of Vitality is funding 4 extra regional DAC hubs with billions of {dollars} in seed cash.
Now, the Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Expertise (NIST) goals to facilitate the event of this quickly rising expertise that the Worldwide Vitality Company (IEA) says will probably be a “key technology” for combating global warming.
NIST scientists have developed a high-precision testing equipment for benchmarking the efficiency of the supplies, referred to as sorbents, utilized in DAC vegetation to entice and take away carbon from the air.
The equipment will allow the company to develop research-grade check materials (RGTM) sorbents for the DAC business. These reference supplies will probably be examined within the equipment and validated to take away a certain quantity of CO2 from a given quantity of air.
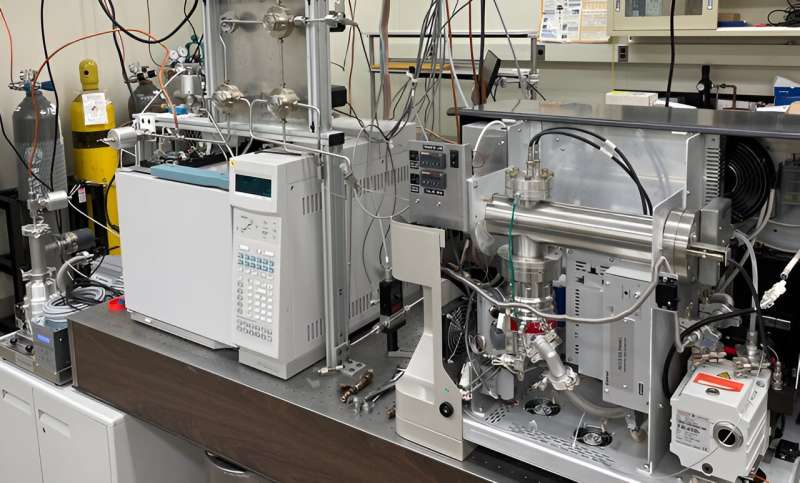

Two of the apparatuses designed to check supplies utilized in DAC vegetation to entice and take away carbon from the air. Credit score: J. Manion/NIST
Corporations could have the choice of utilizing the RGTMs to calibrate their tools, ensuring they get the identical outcomes as NIST does once they check the company’s supplies. They’ll additionally use the supplies as a part of their analysis and growth course of, benchmarking the carbon-removal efficiency of their supplies in opposition to NIST’s.
“Our test and the RGTMs will allow for the critical and impartial evaluation of new, emerging DAC materials and a more comprehensive understanding of their performance,” stated NIST analysis chemist Sean McGivern. “We hope this will help advance the development of measurements and standards for the DAC industry.”
World warming outcomes when greenhouse gasestogether with carbon dioxidemethane, nitrous oxide and fluorinated compounds, accumulate within the environment. The gases soak up infrared radiation, resulting in larger temperatures close to the Earth’s floor.
There are pure strategies for eradicating carbon from the air, comparable to planting bushes and soil restoration. Nonetheless, scientists imagine further approaches will probably be wanted to battle world warming.
Usually, DAC vegetation use big followers to suck in air, which is then pushed by a filter containing sorbents. When heated (or by one other technique), the sorbent materials releases, or desorbs, the carbon. The carbon could be buried deep within the floor or repurposed for industrial makes use of comparable to concrete and artificial fuels.
Sorbents can both be solids or liquids. NIST’s testing equipment is just for strong sorbents, comparable to ion trade resin, polymer-impregnated mesoporous silica (PIMS) and metal-organic frameworks (MOF).
The newly constructed DAC plant in California can take away a most of 1,000 metric tons of CO2 per 12 months, the equal of eradicating roughly 200 automobiles from the highway. However by 2050, the IEA predicts many extra DAC services will probably be constructed with the mixed potential to take away almost 1 billion metric tons of CO2 per 12 months.
“We need to scale this technology up by approximately six orders of magnitude to have the needed climate impact,” says Pamela Chu, coordinator of NIST’s Carbon Accounting and Decarbonization Program. “More research and development are needed to make this technology as efficient and economically viable as possible.”
NIST’s testing equipment, first described in 2023 within the journal Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Analysisis designed to place strong sorbents by their paces. Analysis chemist Jeffrey Manion, who helped create it, stated it supplies amongst “best-in-the-world measurements” to find out “exactly how well the material does in adsorbing carbon.”
For the RGTMs, the primary of that are anticipated subsequent 12 months, NIST researchers will check sorbents generally used within the DAC business.
An RGTM is an early-stage reference materials that may result in a normal reference materials (SRM), which is extra totally characterised and measured and comes with a certificates of study.
NIST analysis chemist Elisabeth Mansfield stated the company would possibly finally develop SRMs for DAC sorbents, however at this level, is working to supply the fast-growing and extremely aggressive business with reference materials as rapidly as doable.
“Many companies right now are developing new types of sorbents,” she stated. “They will want to know they work in the lab before they scale up. These RGTMs will let them test their lab equipment and give them confidence in their measurements.”
This story is republished courtesy of NIST. Learn the unique story here.
Quotation:
Crew develops new testing system for carbon seize in battle in opposition to world warming (2024, April 26)
retrieved 26 April 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-04-team-carbon-capture-global.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.