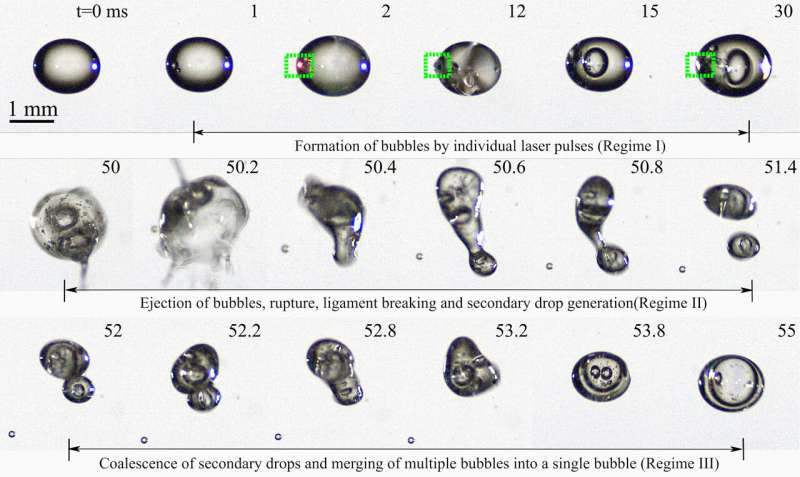
Footage thats exhibits how bubbles kind in a diesel droplet by means of the interplay of a number of femtosecond laser pulses. The method is documented in a high-speed digicam. Credit score: Yogeshwar Nath Mishra/College of Gothenburg
By finding out how bubbles kind in a drop of biodiesel, researchers on the College of Gothenburg might help future engines get probably the most power out of the gas.
In an internal combustion enginethe gas is distributed in small droplets in injection valves to maximise combustion.
Within the engine, the gas droplets are pressurized to show into gasoline and burn. When gasoline is shaped, bubbles kind contained in the droplets and it’s these that the researchers on the College of Gothenburg have studied utilizing femtosecond lasers.
Much less emissions
“The bubbles have a significant impact on the atomization of biodiesel in engines. Therefore, our research is very important to address fundamental questions about the efficiency of the biodiesel engine,” says Dr. Yogeshwar Nath Mishra, who led the examine on the College of Gothenburg along with Professor Dag Hanstorp.
Researchers try to grasp how and when the bubbles kind within the gas droplets. In the long run, this data may result in the event of a extra environment friendly engine that burns extra gas than at the moment, leading to much less environmentally dangerous emissions.
“Research on biodiesel is crucial in our transition from fossil fuels to combat climate change. In engines, bubbling affects fuel combustion and contributes to the formation of larger droplets that do not evaporate and burn completely, leading to increased emissions,” says Dr. Nath Mishra.
The droplet is levitated acoustically
Finding out bubble formation in engine injection valves is troublesome due to their construction, with slim channels in steel our bodies. However with the newest know-how, physicists can arrange an experiment within the lab that enables them to review the method in a millimeter-sized drop of biodiesel. First, a gas droplet is levitated, i.e. trapped within the air, utilizing a standing sound wave.
“We then energize the droplet with our femtosecond laserwhich focuses light energy at a point inside the droplet for a very short time, 100 femtoseconds, 10-13 seconds. This forms the gas bubbles, the number, growth and fine distribution of which are studied using a high-speed camera,” explains Hanstorp, Professor of Physics on the College of Gothenburg.
Yogeshwar Nath Mishra, former researcher on the College of Gothenburg. Credit score: Max Gmelch
Many functions
The outcomes, printed in Scientific Studieshave supplied important insights into the phenomenon of bubble formation that aren’t solely helpful within the growth of extra environment friendly fuels and combustion engines.
“Bubble formation is important in industries such as chemical engineering for example carbonated drinks, ultrasonic imaging, boiling processes for heat transfer and processes such as gas release from water bodies and cloud formation. But what we have achieved is basic research. There is still a lot of development to be done before it can be used,” says Hanstorp.
Extra info:
Vishal S. Jagadale et al, Bubble dynamics and atomization of acoustically levitated diesel and biodiesel droplets utilizing femtosecond laser pulses, Scientific Studies (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-57802-8
Offered by
University of Gothenburg
Quotation:
Researchers examine levitating diesel and biodiesel droplets for extra environment friendly biofuel motors (2024, Could 15)
retrieved 15 Could 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-05-levitating-diesel-biodiesel-droplets-efficient.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.