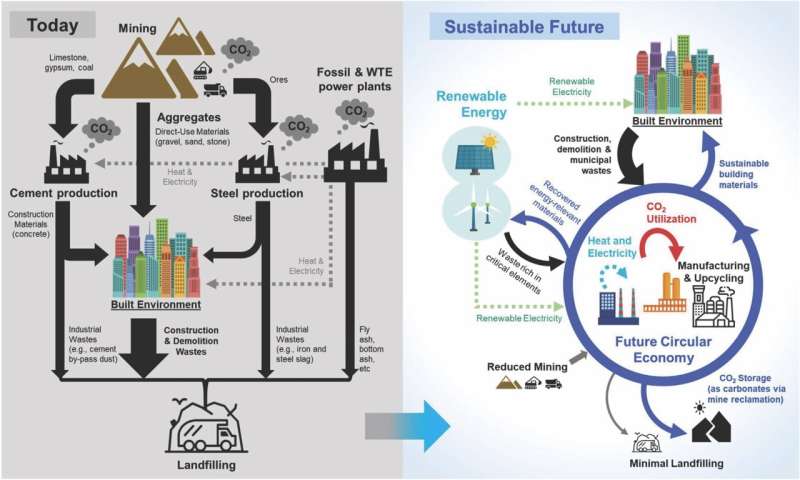
The way forward for the constructed atmosphere throughout the round economic system. Credit score: Frontiers in Power Analysis (2024). DOI: 10.3389/fenrg.2024.1388516
The constructed atmosphere—infrastructure for buildings and transportation—at present produces a big portion of worldwide carbon dioxide emissions, however new applied sciences have the potential to rework the constructed atmosphere from a carbon supply to a carbon sink.
Researchers launched suggestions on how the development sector can incorporate new supplies and processes to assist scale back or seize and reuse CO2 emissions in a latest perspectives piece revealed in Frontiers in Power Analysis.
As people proceed to emit CO2 into the environment, warming the planet and causing climate changethe U.S. and lots of different nations around the globe are making commitments to scale back their carbon footprint.
Buildings and the construction sector account for about 39% of energy-related global CO2 emissions annuallypositioning the constructed atmosphere as a serious focus of decarbonization efforts. For that reason, the U.S. Federal Sustainability Plan set forth an formidable objective to realize net-zero emissions buildings by 2045.
“Climatologically, we are running out of time. We can no longer continue to build the way we have always done,” mentioned Volker Sick, Director of the World CO2 Initiative and the DTE Power Professor of Superior Power Analysis on the College of Michigan and contributing writer on the research.
The multidisciplinary crew emphasised that we have to think twice about development now as infrastructure lifespans are sometimes 50 to 100 years lengthy.
“Any opportunities we miss now, we miss for a century,” mentioned Sick.
At the moment, the growing old constructed atmosphere within the U.S. is way beneath sustainability requirements, incomes a C- on the American Society of Civil Engineers’ infrastructure report card in 2021. Changing deteriorating infrastructure gives a chance to suppose strategically about creating the constructed atmosphere with climate change mitigation in thoughts.
“Our living and working spaces could fundamentally shift the battle against climate change, playing a pivotal role for generations to come. Embracing these innovations isn’t just technologically interesting, it’s imperative for a sustainable future,” mentioned Ah-Hyung “Alissa” Park, the Ronald and Valerie Sugar Dean of the UCLA Samueli College of Engineering and corresponding writer of the research.
Adapting to the altering local weather and adhering to new insurance policies would require collaboration amongst trade professionals concerned in the complete constructed atmosphere life cycle—from mining uncooked supplies to demolition.
There isn’t any single answer to reaching zero-carbon buildings and even lowering constructed atmosphere CO2 emissions. The analysis crew highlights new applied sciences to scale back or seize CO2 emissions throughout 4 phases of a construction’s life cycle—processing supplies, development, constructing use and demolition.
Processing supplies
World urbanization developments create an enormous demand for concrete, however standard supplies like Odd Portland Cement—a concrete element—have a excessive carbon depth with about 0.6 tons of CO2 emitted for every ton of cement produced.
Cement dietary supplements like fly ash—a waste product from coal energy crops—are already used to partially replace cementwhich reduces the necessity to mine raw materials. Nonetheless, to satisfy the massive demand for concrete, another cement should be abundantly out there worldwide.
For that reason, engineers are creating magnesium-based cements, slightly than the standard calcium-based variations, as magnesium is abundantly out there within the Earth’s crust and seawater. Uncooked magnesium supplies will be harvested emission-free by way of electrochemical pathways, and magnesium-based cements may even be captured from wastewater sludge.
Metal is one other excessive demand materials with a big carbon footprint, producing 1.91 tons of CO2 per ton of crude steel cast. Biofibers, CO2-based polymer fibers, carbon fibers and carbon nanotubes have been examined as metal options, aiming to scale back CO2 emissions whereas bettering corrosion resistance. Carbon nanotubes will be made from seaweed contaminated with plasticproviding a further advantage of upcycling waste supplies.
Regardless of the developments in metal replacements, in some instances, metal’s nice energy and ductility make it irreplaceable. As a substitute, adjustments to the metal manufacturing course of may help scale back CO2 emissions (e.g., switching fuels from coke and coal to fuel and biomass, changing furnaces with environment friendly electrical arc furnaces and incorporating hydrogen into steelmaking).
Building
With new supplies come new development methods. Additive manufacturing, recognized generally as 3D printing, accompanied by lean manufacturing to reduce waste, may help develop future buildings and infrastructure incorporating the brand new supplies talked about above.
“Concrete 3D printing presents an unparalleled alternative to advance a brand new development paradigm, harnessing the mixing of novel supplies like low CO2 cement, CO2 sequestered fillers and unconventional bio-based binders.
“These materials not only align with the performance demands of 3D printing but also introduce possibilities beyond the constraints of conventional construction methods,” mentioned Mahmoud Taha, a Distinguished Professor and Regents’ Lecturer on the Gerald Might Division of Civil, Building & Environmental Engineering on the College of New Mexico and contributing writer on the research.
“The primary hurdle lies in the substantial investment required to catalyze this breakthrough within an inherently conservative industry,” added Taha.
Building methods may actively scale back CO2 emissions by way of utilizing CO2 as a feedstock or capturing it. CO2 use, like curing concrete in a CO2 environmentreduces the carbon footprint of supplies whereas producing a stronger materials.
CO2 seize from development waste straight converts CO2 into stable carbonates in a course of referred to as carbon mineralization. These stable carbonates can then be recirculated into the supply chain as constructing supplies or saved for deep CO2 sequestration.
“Carbon dioxide capture and use offers us the opportunity to help stabilize the climate, and to add critically needed jobs especially in underserved regions of the world. These are all urgent needs that require swift and large-scale action,” mentioned Sick.
Constructing use
As soon as constructed, the constructed atmosphere continues to eat vitality to accommodate occupants or actions. Buildings within the U.S. account for three-fourths of electricity consumptionproviding a chance to implement impactful vitality use adjustments.
Enhancements to sensing and computational capabilities can improve a constructing’s demand flexibility, or potential to handle its vitality demand in accordance with electrical grid situations, native local weather or person wants.
Multi-functional supplies may enhance constructing sustainability, like photo voltaic cells in roofing and home windows to generate vitality on-site or phase-changing supplies as insulation to enhance warmth modulation.
Demolition
Higher demolition practices may help develop well-separated waste streams to successfully get better supplies, like rare-earth components for vitality use or industrial alkaline wastes (e.g., iron and metal slag, purple mud, waste-to-energy ashes, mine tailings or waste concrete) for carbon seize by way of mineralization.
Upcycling waste aggregates may optimistically recapture up to six gigatons of CO2 per year by 2050. General, creating circularity for development supplies will develop a sustainable future economic system.
To attain the shift from a carbon-emitting to a carbon-storing trade, applied sciences should mature—rising provide chains and manufacturing bases—whereas coverage adjustments assist financial viability.
Extra data:
Ah-Hyung Alissa Park et al, Challenges and alternatives for the constructed atmosphere in a carbon-constrained world for the following 100 years and past, Frontiers in Power Analysis (2024). DOI: 10.3389/fenrg.2024.1388516
Quotation:
Seize and reuse alternatives for CO₂ within the development sector within the subsequent 100 years (2024, Might 20)
retrieved 20 Might 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-05-capture-reuse-opportunities-sector-years.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.