by KeAi Communications Co.
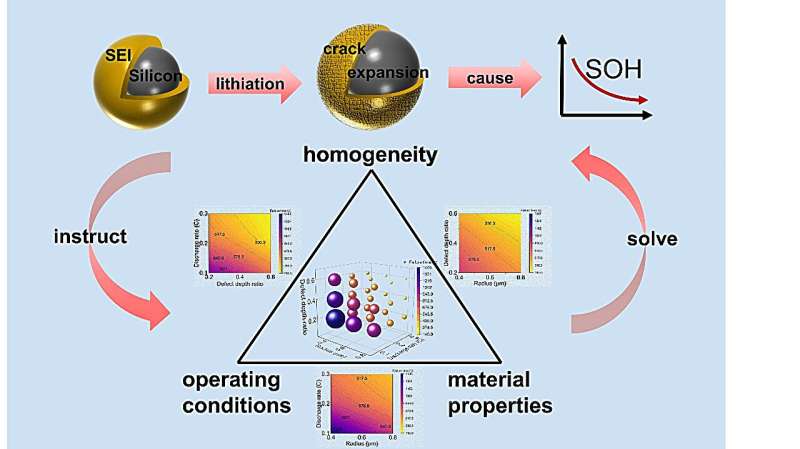
Impact of three elements on SEI stability. Credit score: Junjie Ding, Xueyan Li, Lili Gong, Peng Tan.
Lithium-ion batteries are extensively utilized in new vitality automobiles on account of their low self-discharge charge and lengthy cycle life. At present, the anode materials of business lithium-ion batteries primarily adopts graphite, with a theoretical capability of solely 372 mAh g-1—which has steadily failed to satisfy the rising demand for vitality density.
Silicon has been extensively studied by advantage of its excessive theoretical capability of 4,200 mAh g-1. Nonetheless, silicon produces quantity modifications of as much as 300% throughout lithiation and delithiation, and the following mechanical degradation and capability loss hinder functions.
To cut back the hostile results brought on by mechanical deformation, silicon construction optimization has been intensively investigated and has successfully improved the biking efficiency. Nonetheless, the long-term improvement of silicon-based vitality storage supplies requires not solely steady electrodes, but additionally a steady interphase between electrodes and electrolytes.
Natural electrolytes, that are extensively utilized in typical lithium-ion batteriescut back on the anode floor to type a skinny movie known as strong electrolyte interphase (SEI).
Sadly, drastic quantity modifications in silicon can result in the buildup of stress and destruction of the SEI, which is able to subsequently regenerate on the uncovered anode floor, enormously rising irreversible lithium and electrolyte consumption and inflicting capability degradation. Due to this fact, it’s notably essential to stabilize the mechanical properties of SEI on silicon supplies.
To that finish, the Superior Energy Analysis Group led by Peng Tan of the College of Science and Expertise of China (USTC) has initiated a modeling examine on the mechanical stability of SEI from three views: electrode materials properties, SEI geometrical properties, and battery working circumstances. The work has been published in Superior Powder Supplies.
The modeling was based mostly on the continuum mechanics mannequin, coupled with the electrochemical mass switch course of.
The staff quantitatively analyzed the consequences of three elements on SEI stability and battery capability utilization by constructing a mannequin of particular person electrode particles.
They came upon that as a way to enhance SEI stability, spherical silicons with smaller particle sizes ought to be used as a lot as doable within the design of electrode supplies. When it comes to SEI geometry, it’s notably essential to artificially assemble SEI with a uniform construction, whereas in terms of cell operation, excessive multiplicity will convey better capacity utilization however will not be conducive to SEI stability.
The findings reveal SEI’s high-stability design and operation technique and can information the event of silicon-based vitality storage batteries with excessive biking stability.
Extra data:
Junjie Ding et al, Investigating the failure mechanism of strong electrolyte interphase in silicon particles from an electrochemical-mechanical coupling perspective, Superior Powder Supplies (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.apmate.2024.100200
Supplied by
KeAi Communications Co.
Quotation:
Investigating failure mechanisms of strong electrolyte interphase in silicon particles (2024, Might 22)
retrieved 22 Might 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-05-failure-mechanisms-solid-electrolyte-interphase.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.