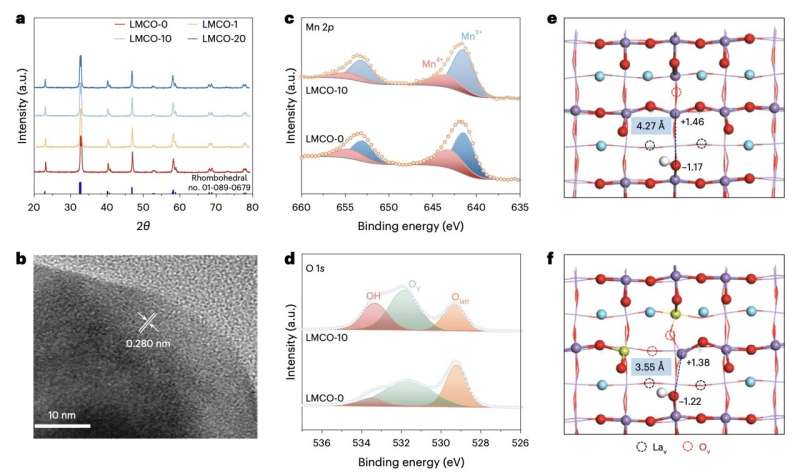
Structural characterization of the catalyst. a, PXRD patterns of LMCO samples (θ is half of the diffraction angle). b, HRTEM picture of LMCO-10. c, XPS spectra of Mn 2p for LMCO-0 and LMCO-10 samples. d, XPS spectra of O 1s for LMCO-0 and LMCO-10. e,f, SFLPs on LMCO-0 (e) and LMCO-10 (f). Pink, white, purple, yellow and blue colors symbolize O, H, Mn, Cu and La atoms, respectively. Credit score: Nature Power (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41560-024-01541-7
Ethylene (C2H4) is a extremely flammable compound extensively utilized in quite a few settings, together with the manufacturing of packaging and plastic-based objects, the chemical business, agriculture and well being care. Creating efficient and sustainable strategies to provide ethylene on a big scale might assist to fulfill the rising demand for this versatile hydrocarbon.
One potential manner of manufacturing ethylene entails changing the hydrocarbon ethane (C2H6), which is plentiful in pure gasoline, into ethylene and hydrogen. Proposed strategies to do that, nevertheless, require substantial electrical energy and are thus related to a big carbon footprint.
Researchers at Soochow College, College of Toronto and different institutes just lately launched a brand new method to provide ethylene by way of the solar-powered photocatalytic dehydrogenation of ethane utilizing the perovskite oxide LaMn1−xWhose3. This perovskite, outlined in a paper published in Nature Powerpossesses favorable properties that make it a promising selective photocatalyst for changing ethane to ethylene and hydrogen utilizing photo voltaic or LED gentle.
“Industrial-scale ethylene production occurs primarily by fossil-powered steam cracking of ethane—a high-temperature, high-energy process,” Rui Music, Guanshu Zhao and their colleagues wrote of their paper. “An alternative, photochemical, pathway powered by sunlight and operating under ambient conditions could potentially mitigate some of the associated greenhouse gas emissions. We report the photocatalytic dehydrogenation of ethane to ethylene and hydrogen using LaMn1−xCuxO3.”
Music, Zhao and their colleagues confirmed that utilizing the perovskite oxide LaMn1−xCuxO3 as a photocatalyst, they may effectively convert ethane into ethylene and hydrogen with out the necessity for exterior warmth sources. This conversion will be achieved utilizing photo voltaic or LED lights, thus leading to decrease carbon emissions.
“This perovskite oxide possesses redox-active Lewis acid sites, comprising Mn(III) and Mn(IV), and Lewis base sites, comprising O(-II) and OH(-I), collectively dubbed surface-frustrated Lewis pairs,” the staff wrote. “We find that tuning the relative proportions of these sites optimizes the activity, selectivity and yield for ethane dehydrogenation.”
The researchers evaluated their solar-powered ethylene manufacturing method utilizing a rooftop prototype gadget and attained exceptional ethylene manufacturing charges. As well as, they carried out complete technical and financial analyses, which highlighted the sizable financial potential of their proposed answer.
“The highest ethylene production rate and ethane conversion achieved were around 1.1 mmol g−1 h−1 and 4.9%, respectively,” Music, Zhao and their colleagues wrote. “We show a simple outdoor prototype to demonstrate the viability of a solar ethylene process. In addition, techno-economic analysis revealed the economic potential of an industrial-scale solar ethylene production from ethane.”
To maximise the absorption of sunshine and decrease losses, the photocatalyst and photoreactor supporting this ethane conversion course of will must be fastidiously engineered. But findings gathered up to now are extremely promising, suggesting that this new perovskite oxide-based photocatalyst might show advantageous for the longer term large-scale manufacturing of ethylene.
Of their subsequent research, Music, Zhao and their colleagues plan to additional examine the efficiency of their photocatalyst and photoreactor, particularly exploring their results on catalytic reactions. As well as, they hope to additional enhance photochemical activation, gentle seize and light-weight transport charges, to additional enhance the LaMn1−xCuxO3 perovskite’s photocatalytic effectivity.
Extra info:
Rui Music et al, Ethylene manufacturing by way of photocatalytic dehydrogenation of ethane utilizing LaMn1−xCuxO3, Nature Power (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41560-024-01541-7
© 2024 Science X Community
Quotation:
A perovskite for the environment friendly photocatalytic conversion of ethane into ethylene and hydrogen (2024, June 19)
retrieved 19 June 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-06-perovskite-efficient-photocatalytic-conversion-ethane.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.