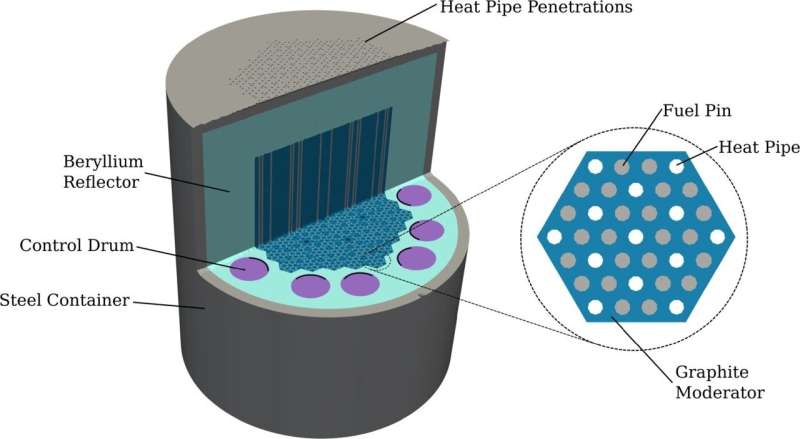
Fundamental structure of the Westinghouse eVinci microreactor design with an enlarged gasoline flake. Credit score: Worth et al., 2024.
An actual-time, 3D temperature map of the within of a nuclear microreactor for improved security monitoring was reconstructed utilizing a newly-established theoretical basis to judge foundation features, which might be mixed to explain elementary traits in knowledge, in accordance with a brand new College of Michigan examine.
The outcomes, published in Utilized Mathematical Modellingare relevant wherever “big data” analytics are required because the reconstruction strategies are fitted to high-resolution distributions in 3D.
“Most work in sparse reconstruction methods focus on time-dependent digital signals, but this study focuses on distributions which exist in physical space,” stated Dean Worth, a doctoral scholar of nuclear and radiological sciences at U-M and corresponding creator of the examine.
Whereas analysis discovered that common foundation features will not be correct sufficient for real-world microreactor temperature monitoring, the workforce recognized methods to enhance them.
Nuclear microreactors—small nuclear reactors capable of be hauled by a semi-tractor trailer—can function independently or as a part of {an electrical} grid. These compact reactors can generate as much as 20 megawatts of thermal power that can be utilized instantly as warmth or transformed to electrical energy.
The decrease upfront prices and smaller siting necessities of microreactors ought to open up new markets for nuclear powerwhich has important potential to enhance renewable power in transitioning to a decarbonized electrical grid.
“One of the main challenges to achieving this is the ability to ensure that we know what’s going on inside the reactor at any given time,” stated Brendan Kochunas, an affiliate professor of nuclear engineering and radiological sciences at U-M and senior creator of the examine.
Capable of go for years with out refueling, nuclear microreactors supply each reliability and operational flexibility to be used in pure catastrophe reduction, navy operations or remote areas. Nonetheless, working in distant areas calls for refined monitoring methods to make sure security.
“Digital twins, meaning a representation of the physical reactor reconstructed from sensor data, are an exciting new prospective technology which may improve both the safety and economic viability of nuclear microreactors,” stated Worth.
A high-resolution, 3D reconstruction of temperature distributions inside a heat pipe nuclear microreactor permits monitoring methods to trace metrics of efficiency and security standing—together with materials degradation, doppler suggestions and warmth pipe efficiency—whereas decreasing the necessity for prime price labor from human operators.
“Earlier than deployment, we should be certain that surveillance utilizing digital twins gives correct data for protected operation inside core working limits,” stated Majdi Radaideh, U-M assistant professor of nuclear engineering and radiological sciences and contributing creator of the examine
Sometimes, reconstruction strategies measure temperature with sensors positioned at numerous factors throughout the reactor and interpolate to estimate temperature in areas circuitously measured.
As sparse strategies assemble the temperature distribution utilizing the bottom variety of elementary modes, or patterns throughout the knowledge, numerous approaches to defining these modes can considerably impression the standard of the reconstruction. This examine gives pointers for the analysis of those approaches with an indication on generalized foundation features.
This methodology goals to scale back computational complexity and the quantity of sensor data required whereas sustaining accuracy. The pc-memory conscious nature of the strategies might be significantly helpful when offering detailed data to digital twin methods with restricted computational capabilities.
The researchers evaluated the strategy with a multiphysics simulation—involving a number of bodily processes like nuclear reactions, thermodynamics and fluid dynamics—utilizing generalized foundation features.
Though the strategy efficiently captured broad traits, the generalized foundation features finally fell quick on account of elementary traits of the reactor system together with the spatial variation in warmth switch habits in supplies.
Transferring ahead, these shortcomings might be addressed utilizing tailor-made foundation features, which means foundation features created particularly from precalculated temperature distributions for that microreactor. This may improve accuracy with strong mathematical integrity.
“Our methods are particularly well suited for remote operation as they take computer memory into account, which will be useful for providing detailed information to digital twin monitoring systems with limited computational abilities,” stated Worth.
Extra data:
Dean Worth et al, Simplified matching pursuits utilized to 3D nuclear reactor temperature distribution building, Utilized Mathematical Modelling (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.apm.2024.04.011
Supplied by
University of Michigan College of Engineering
Quotation:
Actual-time modeling of 3D temperature distributions inside nuclear microreactors to enhance security methods (2024, June 28)
retrieved 28 June 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-06-real-3d-temperature-nuclear-microreactors.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.