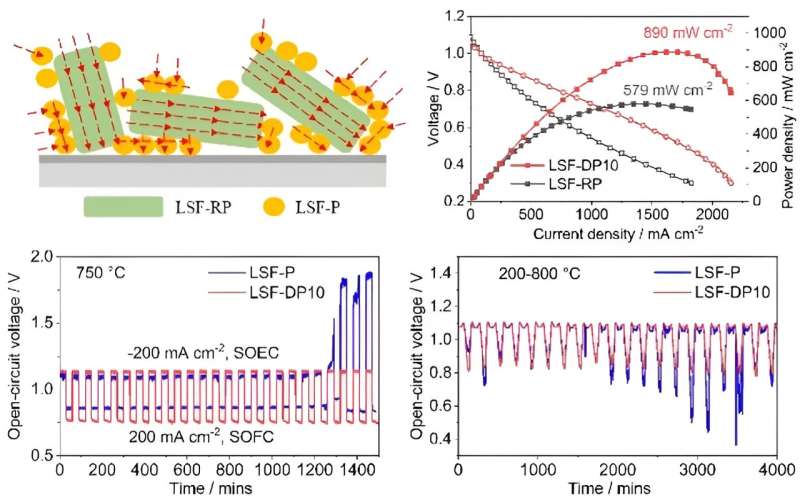
Schematics of cost transport path of the composite air electrode. The present-voltage and current-power density curves of the gasoline electrode-supported cell with LSF-RP and LSF-DP10 composite air electrode in SOFC mode. The cost and discharge cycles of the cell with LSF-DP10 and LSF-P electrode at 750 °C. The present density and open-circuit voltage of the gasoline electrode-supported cell with LSF-P and LSF-DP10 composite air electrode throughout thermal biking with a temperature ramp of 10 °C min-1 between 200 and 800 °C. Credit score: Journal of Superior Ceramics (2024). DOI: 10.26599/JAC.2024.9220938
Stable oxide gasoline cell (SOFC) is a extremely environment friendly and clear superior vitality conversion know-how that converts chemical vitality immediately into electrical vitality by means of electrochemical reactions and might be extensively used for distributed and stationary energy technology.
Within the sensible utility course of, it’s vital to contemplate the consumer’s operational necessities and the upkeep demand. This may increasingly topic the machine to situations the place temperature fluctuations are frequent and pronounced. For instance, in residential functions, the SOFC system might bear frequent cycles of activation and deactivation in accordance with the house owner’s necessities.
Moreover, the temperature of SOFC might change throughout operation. As an example, when harnessing electrical energy from waste heat generated by industrial processes and thermal energy crops, the SOFC might expertise unstable warmth provide. Moreover, substantial diurnal temperature variations within the SOFC’s operational area or extreme meteorological situations, equivalent to excessive winds and snowfall, can result in vital temperature fluctuations.
The mismatch within the TEC of the completely different SOFC elements can result in the technology of thermal stresses throughout temperature fluctuations. These stresses might compromise the integrity of the interfaces between elements, thereby degrading the SOFC’s energy output. Consequently, making certain thermal cycle stability is a crucial problem that should be addressed to attain the profitable commercialization of SOFC know-how.
Not too long ago, a crew of fabric scientists led by Liangzhu Zhu from Key Laboratory of Superior Gas Cells and Electrolyzers Expertise of Zhejiang Province, Ningbo Institute of Supplies Expertise and Engineering, Chinese language Academy of Sciences, China proposed the only perovskite oxide adorned R-P structured oxide could possibly be synthesized by a self-assembly methodology, with the intention of enhancing the catalytic exercise of R-P structured oxides whereas concurrently preserving their stability. This work not solely exhibits the superb enlargement matching between the strontium lanthanum ferrate and electrolyte, but additionally reveals its appreciable potential as a aggressive air electrode for SOFC.
The crew printed their work within the Journal of Advanced Ceramics on July 1, 2024.
“On this report, we synthesized dual-phase La0.8Sr1.2FeO4+d and La0.4Sr0.6FeOthree-D by the easy self-assembly methodology. The one perovskite oxide, La0.4Sr0.6FeOthree-D (LSF-P), with cubic construction and excessive catalytic exercise was launched to facilitate cost transport throughout the R-P structured oxides La0.8Sr1.2FeO4+d (LSF-RP) with varied orientations.
“This method overcomes the anisotropy inherent within the construction and concurrently enhances the catalytic exercise of the composite electrode. The intimate hetero-interfaces which will type in situ between LSF-RP and LSF-P particles are anticipated to expedite the cost switch course of, thereby enhancing the ORR kinetics.
“We present the influence of the LSF-P content in dual phase on the phase structure, thermal expansion coefficient, electrode reaction kinetics, single cell performance under thermal cycling and reversible conditions in detail. The obtained results indicate that the incorporation of LSF-P improves the oxygen surface exchange kinetics, reduces the polarization resistance and significantly enhances the single-cell performance without sacrificing the stability of the composite electrode,” stated Liangzhu Zhu, professor at Ningbo Institute of Supplies Expertise and Engineering, Chinese language Academy of Sciences, China.
“The TEC values of R-P oxides are comparable to those of the electrolytes commonly utilized in SOFC. However, it is important to note that R-P oxides exhibit two-dimensional conduction. They demonstrate significant anisotropy in the diffusion of oxygen ions and electrons, with transport predominantly occurring within the a-b plane and minimal movement along the c-axis. Consequently, there is a need to modify the R-P structured material to enhance its charge transfer capability, thereby increasing their catalytic activity, without sacrificing stability for application in SOFCs,” stated Liangzhu Zhu.
The commonest technique for rising the catalytic exercise of R-P oxides is introducing a secondary section. “Mechanical mixing is a comparatively simple methodology for the introduction of secondary section. Whereas mechanical mixing can improve electrode efficiency to some extent, it struggles with attaining a homogeneous distribution of the phases, which in flip restricts the interfacial contact between them. Infiltration is one other different for introducing the second section materials.
“However, it is a cumbersome and time-consuming process that requires multistep operations,” stated Yang Zhang, one of many co-first authors and a postdoctoral researcher at Ningbo Institute of Supplies Expertise and Engineering, Chinese language Academy of Sciences, China.
“The self-assembly synthesis method for fabricating composite supplies is able to yielding thermodynamically secure and homogeneously dispersed dual-phase buildings in a single, streamlined operation. By merely adjusting the ratios of the beginning supplies, the incorporation of the second section might be finely tuned.
“Furthermore, this self-assembly approach holds significant promise for creating numerous heterogeneous structural interfaces within composite air electrodes, which in turn can significantly boost the kinetics of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). Additionally, the method has the potential to greatly enhance the performance of composite air electrodes by optimizing the ORR process,” stated Liangzhu Zhu.
Extra data:
Qihang Ren et al, An modern and facile synthesis route of (La,Sr) 2FeO 4+ δ –La 0.4Sr 0.6FeO 3− δ composite as a extremely secure air electrode for reversible stable oxide cell functions, Journal of Superior Ceramics (2024). DOI: 10.26599/JAC.2024.9220938
Offered by
Tsinghua College Press
Quotation:
Enhancing the efficiency, stability of stable oxide cells through in-situ forming of twin section strontium lanthanum ferrate (2024, July 22)
retrieved 22 July 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-07-stability-solid-oxide-cells-situ.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.