Vary anxiousness is a real concern for hydrogen automobile house owners, manifesting within the tendency of FCEV drivers to refuel when their tanks are simply 30% full. This conduct mirrors the preliminary struggles of electrical car (EV) house owners, who solely overcame their apprehensions by means of the widespread availability of charging stations.
Equally, hydrogen vehicles face the necessity for a complete refueling infrastructure. Nonetheless, past the query of infrastructure lies the problem of station downtime, whether or not attributable to provide shortages or mechanical points. Happily, these hurdles could also be much less daunting than they seem, providing hope for a smoother path to widespread hydrogen automobile adoption.
Lets have a look what kinds of points hydrogen refueling stations are having, what firms make these elements and the way we’re going to get previous these hurdles.
Hydrogen Gas Nozzle Freezing
Hydrogen nozzles usually freeze attributable to hydrogen’s distinctive properties. Throughout refueling, hydrogen fuel is extremely compressed and cooled to round -423°F (-253°C). This excessive chilly causes moisture within the surrounding air to freeze immediately upon contact with the nozzle, doubtlessly inflicting it to stick to the car’s fueling port.
An instance from California illustrates this concern. Mirai house owners encountered instances the place the hydrogen nozzle froze to their car, leading to lengthy waits for technicians to unfreeze the connection. These incidents turned the anticipated fast refuel into a big inconvenience for drivers.
At such low temperatures, even minor moisture may cause ice formation. True Zero skilled this when the nozzle would create a seal round itself, immobilizing the car. This necessitated both:
- Ready for the nozzle to heat sufficiently to detach safely
- Ready for technicians to use options to unfreeze it
Ambient temperatures additional complicate issues. In Alberta, Canada, temperatures dropping under -20°C (-4°F) hinder the fuel switch modules, making operations temperamental. Chilly climate interferes with the purity of hydrogen gas, inflicting condensation that may freeze within the gas traces.
Varied firms like Air Merchandise and True Zero have labored on these nozzle designs. True Zero launched a brand new nozzle designed to attenuate freezing incidents, demonstrating a sensible strategy to mitigating this ongoing drawback.
The broader concern of hydrogen stations continuously experiencing issues stems largely from the nascent stage of hydrogen infrastructure improvement. An absence of complete provide chains means stations usually run out of hydrogen or undergo mechanical failures.
The answer to those issues includes improved know-how and higher infrastructure planning. True Zero’s effort to triple station capacities and roll out new nozzles that resist freezing is a step in the correct course. Moreover, making certain each new station has a backup hydrogen supply can mitigate provide disruptions, providing extra reliability to hydrogen car house owners.
Hydrogen Fueling Station Points
Hydrogen fueling stations face a variety of challenges past nozzle freezing, together with upkeep points, provide chain disruptions, mechanical failures, and insufficient infrastructure.
Upkeep points continuously render stations offline for prolonged intervals. On common, their dispenser systems fail after fewer than 500 useswhich usually leads to a malfunction about each 15 days. In distinction, gasoline stations require corrective upkeep roughly each 21.5 days. This implies hydrogen stations are much less dependable and want repairs extra continuously than conventional gasoline stations.
Provide chain disruptions happen attributable to varied elements, together with the withdrawal of main gamers from the hydrogen market. Shell’s exit resulted in the closure of critical hydrogen stationsleaving important infrastructure gaps. Operators continuously expertise outages due to delayed hydrogen deliveries or problems at manufacturing services.
Mechanical failures contribute to downtime and buyer dissatisfaction. Crucial elements equivalent to compressors and fuel switch modules can fail beneath fixed use or excessive temperatures. True Zero’s expertise illustrates this, the place compressors typically require reboots between fills, including time to the refueling course of.
Easy methods to Refuel a Hydrogen Automobile:
Infrastructure Challenges:
- Only 52 hydrogen refueling stations nationwide in the United States
- Inadequate network to meet growing consumption demands
- Longer travel times to reach operational stations
- New stations take up to 18 months to construct
- Each station costs well over a million dollars
Addressing these problems requires substantial investment in infrastructure, technological innovations to handle extreme conditions, and stronger supply chain partnerships to ensure reliability.
Hydrogen Nozzle Development
Several companies are at the forefront of advancing hydrogen nozzle technology:
Air Products: A leading supplier of atmospheric gases and services, focuses on improving nozzle durability and reliability. Their operational staff provide firsthand insight into the practical challenges faced by hydrogen drivers.
True Zero: Has introduced a new nozzle design aimed at reducing freezing incidents. Their advanced nozzle incorporates high-performance polymers and alloys, which resist extreme cold better than traditional materials, enhancing structural integrity and lifespan.
Iwatani Corporation: Contributes to hydrogen nozzle technology by leveraging advanced materials and engineering to design nozzles that operate efficiently under adverse conditions. Their collaborative efforts have helped propagate improved nozzle designs across multiple refueling stations, particularly in California.
Collaboration between these companies and auto manufacturers like Toyota has been crucial in refining the usability and reliability of hydrogen nozzles. These partnerships ensure compatibility and reliability across different refueling stations and align refueling standards with the operational needs of hydrogen vehicles.
As these companies continue to refine their designs and expand infrastructure, the viability of hydrogen as a sustainable fuel source improves.
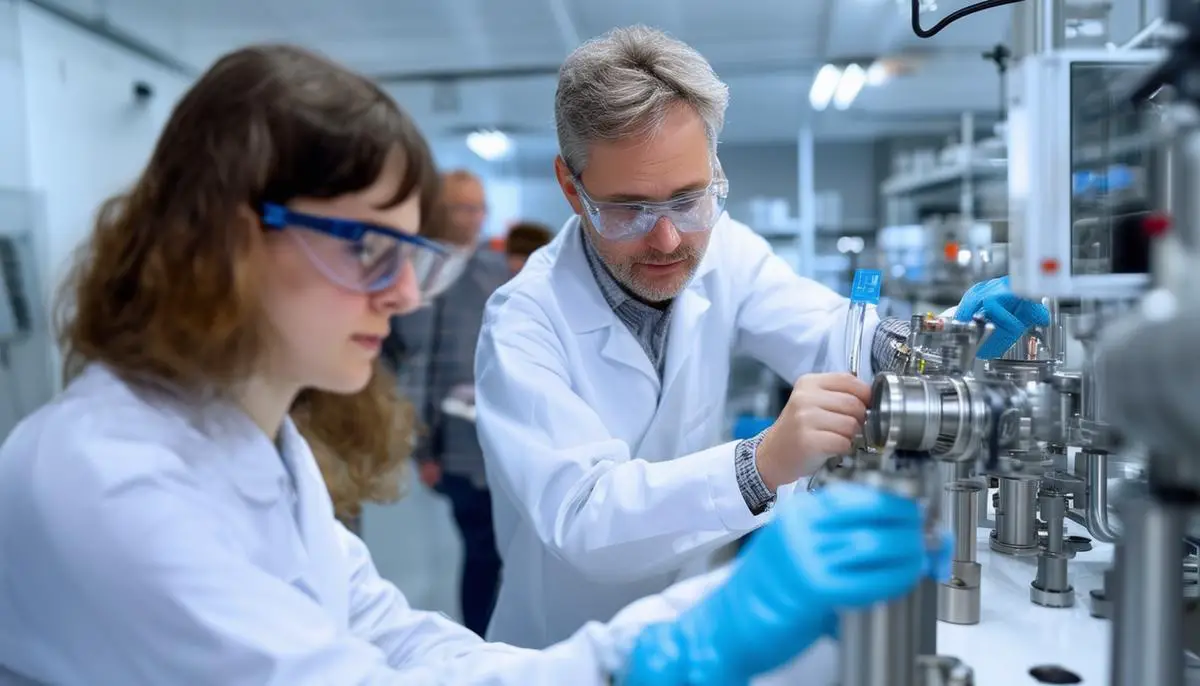

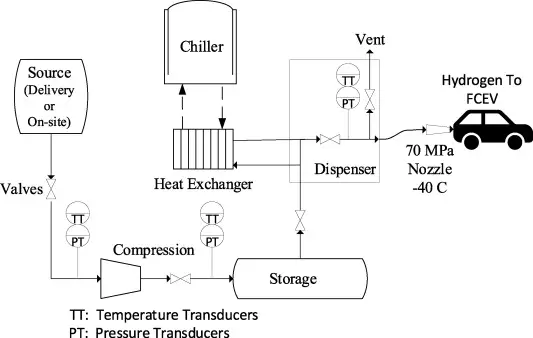
How a Hydrogen Refueling Station Works
A hydrogen refueling station is a facility designed to fill hydrogen-powered vehicles with compressed hydrogen gas. The basic operation involves several key components and processes to ensure efficient and safe refueling.
Key Parts:
-
Compressor: The hydrogen gas, whether produced on-site or delivered from an off-site source, is compressed to the required pressure using a compressor. -
Storage Tank: Once compressed, the hydrogen is stored in a pressurized tank until it is needed for vehicle refueling. -
Pre-cooler: Before filling a vehicle, hydrogen is cooled to -40°C by a pre-cooler. This cooling process is essential to prevent overheating during the transfer of hydrogen into the vehicle’s tank.
Forms of Stations:
On-site Stations: Produce hydrogen directly at the station using resources like city gas and water. - Off-site Stations: Receive hydrogen transported from an external production site.
- Fixed Stations: Operate at permanent locations similar to traditional gas stations.
- Mobile Stations: Mounted on trailers, they can be moved to different locations as needed.
- Integrated Stations: Combine traditional fuel services with hydrogen refueling capabilities.
Course of Overview:
Hydrogen Production/Transportation: Depending on the station type, hydrogen is either produced on-site or transported from another location. - Compression and Storage: The hydrogen is compressed and stored until it’s needed.
- Cooling and Dispensing: The pre-cooled hydrogen is then dispensed into the vehicle’s tank.
Measurements Taken:
To ensure safety and efficiency, several measurements are consistently monitored at hydrogen stations:
- Gas pressure and temperature are measured at various points, including before and after compression and during dispensing.
- The storage system’s state of charge and cycle counts are tracked.
- Vehicle tank temperature, pressure, and volume are recorded during refueling.
These stations are equipped with sensors and controls to manage the flow, pressure, and temperature of hydrogen, ensuring a safe and efficient refueling experience for hydrogen-powered vehicles.

Credit score: Photograph by depositphotos.com
Improving Reliability and Solutions to Hydrogen Fueling Problems
Addressing hydrogen fueling challenges requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Material Innovation: Continued research into more robust and temperature-resistant materials for nozzles and other components.
- Mechanical Reliability: Adoption of advanced compressor technologies with higher operational thresholds and improved maintenance routines.
- Infrastructure Enhancement: Incorporating redundancy into the fueling network and prioritizing rapid deployment of additional stations.
- Regulatory Support: Government policies promoting hydrogen technology development, coupled with financial incentives to accelerate the deployment of advanced refueling stations.
- Industry Collaboration: Shared knowledge and co-development initiatives among major players to tackle specific challenges.
- Best Practices Adoption: Scaling proven models to other regions and incorporating insights from successful international hydrogen networks.
- Long-term Strategies: Investing in smart grid technologies to optimize hydrogen production based on renewable energy availability and embracing digital solutions for predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring of station performance.

The advancement of hydrogen refueling stations is an evolving area, yet one promising approach to optimize their efficiency is the implementation of the PHM (Prognostics and Health Management) model. According to a study, adopting a unified set of maintenance guidelines across all existing stations can significantly minimize downtime for drivers. The key to this strategy is proactive maintenance, which involves initiating each day with thorough equipment check-ups.
As these stations require more technicians trained specifically in hydrogen refueling equipment maintenance, such specialized training is crucial to effectively execute the PHM model and proactive strategies. By addressing potential issues before they escalate, this approach is estimated to reduce costs by up to 30% compared to unscheduled maintenance, as evidenced by findings from other industries.
In conclusionthe adoption of standardized maintenance practices and proactive strategies in hydrogen refueling stations offers substantial benefits in reducing both downtime and operational costs. By drawing on successful preventative maintenance models from other industries, the hydrogen sector can enhance reliability and ensure a smoother refueling experience for drivers, ultimately supporting the wider adoption of hydrogen as a sustainable energy source.