Ethiopia first started producing electrical energy from its mega-dam in February 2022.
Ethiopia stated it has greater than doubled electrical energy manufacturing from its controversial mega-dam on the Blue Nile after two extra generators began operations.
The multi-billion-dollar Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD), lengthy a supply of tensions with downstream nations Egypt and Sudan, is now producing 1,550 megawatts of electrical energy, GERD stated in a submit on X late Tuesday.
“The overall progress of the GERD has now transitioned from construction phase to operation phase,” it stated, including that building of the concrete dam was now full.
“The two turbines generating 400MW each have now started operations, adding to the already functional two turbines generating 375MW each, totalling an output of 1,550MW.”
The dam’s spillways had been additionally releasing an additional 2,800 cubic meters of water to the downstream nations, it added.
Ethiopia first started producing electrical energy on the $4.2-billion challenge, which is situated within the northwest of the nation round 30 kilometers (18 miles) from the border with Sudan, in February 2022.
At full capability, the massive dam—1.8 kilometers lengthy and 145 meters excessive—may generate greater than 5,000 megawatts of energy when all 13 generators are operational.

Ethiopia’s Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed insists the dam ensures downstream nations obtain a gradual water provide.
That might make it Africa’s largest hydroelectric dam and greater than double Ethiopia’s present output.
Addis Ababa deems the GERD important for the electrification and growth of Africa’s second most populous nation.
Based on the World Financial institution, roughly half of the 120 million inhabitants nonetheless doesn’t have entry to dependable electrical energy.
Electrical energy deficit
The dam, which may maintain as much as 74 billion cubic meters of water, has been on the centre of a regional dispute ever since Ethiopia broke floor on the challenge in 2011.
Egypt and Sudan have voiced considerations about its operation with no three-way settlement, fearing it may threaten their entry to very important Nile waters, however on-off negotiations have did not make a breakthrough.
Egypt, which is already affected by extreme water shortage, sees the dam as an existential threat as a result of it depends on the Nile for 97 p.c of its water wants.
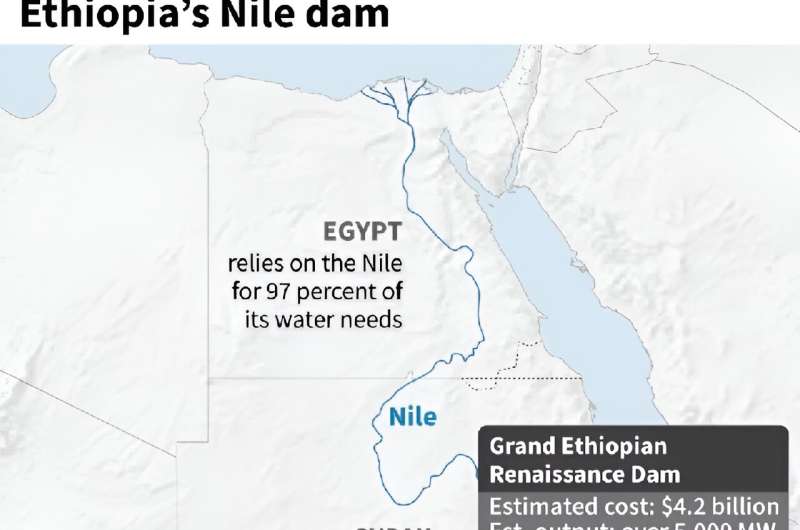
Ethiopia’s dam lies on the Blue Nile.
The place of fragile Sudan, which is at the moment mired in a civil conflict, has fluctuated lately.
Ethiopia insists the dam is not going to cut back the quantity of water flowing downstream.
“The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) plays a crucial role in managing water flowmitigating flood risks, and ensuring that downstream nations receive a steady supply of water, particularly during droughts,” Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed stated in a submit on X on Sunday.
In April, the World Financial institution introduced a plan to assist Ethiopia develop its electrical energy community and diversify into different clear sources, together with photo voltaic, wind, and geothermal energy.
It stated the federal government had made “encouraging progress” on its electrification program and expanded the grid community protection to just about 60 p.c of cities and villages.
“Yet the electricity deficit in Ethiopia continues to exacerbate the poverty situation, preventing far too many people from fulfilling their basic socio-economic needs and limiting access to opportunity,” it stated.
© 2024 AFP
Quotation:
Ethiopia says mega-dam doubles electrical energy output (2024, August 28)
retrieved 28 August 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-08-ethiopia-mega-electricity-output.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
