The transport trade is an integral a part of worldwide commerce. Over the previous 40 years, international maritime commerce has elevated 10X in worth. Similar to different transportation sectors aviation and auto, transport additionally has some degree of carbon emissions.
Within the Introduced Pledges Situation (APS), transport emissions may fall considerably. IEA predicts by 2035, emissions from worldwide transport might drop by practically 60%, and by 2050, they may fall by greater than 90%.
This shift is predicted because the transport trade adopts cleaner fuels like biofuelsammonia, and methanol. By 2050, low-carbon fuels might energy over 80% of worldwide transport.
The Two-Method Method to Decarbonizing Delivery
Decarbonizing the transport trade is essential for assembly international emissions targets. Presently, two main methods are in place that are enhancing vitality effectivity and transitioning to low-emissions fuels. These approaches provide complementary advantages and may considerably reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
Boosting Vitality Effectivity in Delivery
One of many easiest operational measures is “slow steaming,” which includes lowering the common pace of ships. This follow doesn’t require modifications to the vessels however can not directly have an effect on prices. Whereas sluggish steaming can decrease general gasoline consumption, it could additionally enhance operational bills because of a necessity for extra ships to take care of the identical transport capability. That is notably vital for sectors counting on just-in-time supply methods.
Many applied sciences to enhance vitality effectivity are already obtainable. New laws just like the Carbon Depth Index (CII) require ships to decrease their emissions over time, encouraging each new ships and retrofits to undertake energy-saving options.
There are a number of technical measures that may be carried out to enhance a ship’s gasoline effectivity. Some examples are:
- Inflexible Sails and Rotor Sails: Utilizing wind for propulsion can cut back gasoline utilization.
- Waste Warmth Restoration: Capturing and reusing warmth from the engine improves general effectivity.
- Anti-Fouling Hull Coatings: These stop the expansion of marine organisms on hulls, enhancing efficiency.
- Hull Optimization: Streamlining hull shapes minimizes water resistance, boosting pace and effectivity.
- Air Lubrication Techniques: Producing microbubbles underneath the hull reduces friction.
Since 2010, the vitality effectivity design of latest ships has improved by 30-50%, pushed by initiatives such because the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) Vitality Effectivity Design Index (EEDI). Whereas present vitality effectivity applied sciences are commercially obtainable, they aren’t adopted very simply.
IEA predicts that effectivity positive factors of 5-10% or extra by 2030 are possible with extremely superior energy-efficient strategies.
Now talking about prices; the funding required for energy-efficient upgrades varies extensively, however they typically repay by means of gasoline financial savings. As an example, hull type optimization prices about $250,000 and may increase vitality effectivity by 7.5%. Extra intensive retrofits, resembling kite sails, can price as much as $1.2 million however provide smaller positive factors.
Then again, a brand new bulk service constructed with cutting-edge know-how might be 40% extra environment friendly than one inbuilt 2023, whereas a retrofitted container ship may obtain about 30% in vitality financial savings.
Transitioning to low-emission fuels
Whereas bettering vitality effectivity is important, it can’t fully remove emissions. For this reason the transport trade should additionally shift to low-emissions fuels to succeed in its web zero goal.
Promising choices for low-emission fuels are:
- Biodiesel: Can be utilized in current diesel engines with little modification.
- Biomethane: A renewable different appropriate with LNG engines.
These drop-in fuels have limitations based mostly on the supply of sustainable biomass and excessive manufacturing prices. Regardless of being cheaper to implement, their general prices could also be larger because of market competitors, notably from aviation.
Superior Options: Methanol, Ammonia, and Hydrogen
- Methanol: Gaining reputation, methanol-fueled vessels are on the rise. In 2023, the primary methanol-fueled container ship with a dual-fuel engine started operation. Nevertheless, methanol requires modifications to ship engines and tanks.
- Ammonia: Though at a decrease know-how readiness degree, ammonia presents a promising future because of its lack of carbon sourcing necessities. Roughly 20 ammonia-powered vessels are on order, with deliveries anticipated by 2026.
- Hydrogen: Over 20 hydrogen-fueled vessels are at present operational or deliberate. Security tips for hydrogen utilization in transport are being developed, aligned with these for ammonia.
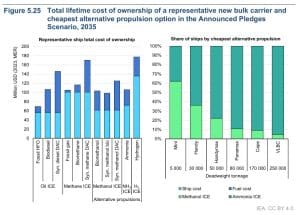
Delivery corporations might want to contemplate the entire price of possession, together with gasoline prices over a vessel’s lifespan when deciding which gasoline know-how to undertake. Whereas methanol could also be cost-effective for smaller vessels, ammonia tends to be extra economical for bigger ships.
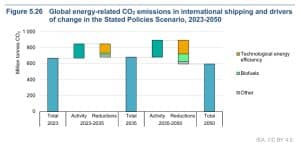
Future Emissions Trajectories
Worldwide maritime transport emissions have risen sharply lately, with a peak of 0.67 Gt CO2 in 2023, accounting for round 2% of worldwide energy-related CO2 emissions. Emissions reductions will closely depend upon insurance policies that promote sooner effectivity positive factors and the change to low-emission fuels.
In a situation aligned with the newest IMO GHG Technique, emissions might be decreased by greater than 90% by 2050 in comparison with 2023 ranges, primarily by means of low-emissions fuels like ammonia.
As transport exercise is projected to extend considerably, implementing low-emission methods turns into crucial. By 2040, fossil fuel use in transport may drop from practically 100% to lower than 30%.
Nevertheless, the transition to low-emission transport applied sciences would require substantial funding and regulatory assist. Nonetheless, the potential for vital emissions reductions makes it vital for the trade.
Maersk Seals Lengthy-Time period Bio-Methanol Deal to Obtain Zero-Emission in Delivery
Danish transport big A.P. Moller–Maersk has entered a long-term settlement with China’s LONGi Inexperienced Vitality Know-how Co Ltd to buy bio-methanol. This partnership strengthens Maersk’s dedication to zero-emission transport. The press release revealed that,
It’ll meet Maersk’s methanol sustainability necessities together with no less than 65% reductions in GHG emissions on a lifecycle foundation in comparison with fossil fuels of 94 g CO2e/MJ. The bio-methanol provide is ready to start in 2026.
Bio-fuels and e-methanol are rising as go-to alternate options for main fossil gasoline customers, such because the transport trade, because of their scalability and potential for sustainable manufacturing.
Nevertheless, Maersk highlighted that the substantial price distinction between fossil fuels and greener choices stays a major barrier, difficult the transport trade’s progress towards adopting different fuels and reaching net-zero targets.
Disclaimer: Supply of all knowledge and pictures from IEA Energy Technology Perspective 2024
MUST READ: Can Nuclear Power Propel Maritime into a Zero-Emission Era? Maersk to Explore Nuclear for Ships