The profitable completion of 12 high-voltage electrical transmission initiatives within the US West might dramatically cut back the area’s carbon emissions. It might reduce power-sector emissions by 73% from 2005 ranges by 2030, in keeping with a current research by the Pacific Northwest Nationwide Laboratory (PNNL).
The research underscores the vital function that renewable power and transmission infrastructure will play in attaining nationwide local weather objectives, particularly President Biden’s ambition to transition to a 100% carbon-free energy system by 2035.
A Holistic Method to Decarbonization
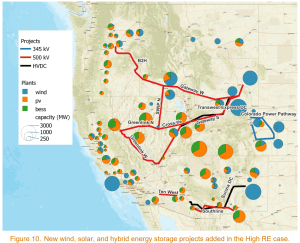
The 12 transmission initiatives might unlock over 72 GW of recent photo voltaic, wind, and battery storage capability. It might considerably contribute to the area’s decarbonization efforts. Importantly, all of those initiatives are both in superior growth, below development, or already operational, making them important parts of the renewable energy enlargement within the West.
The study was carried out in reference to the US Division of Power’s forthcoming Nationwide Transmission Planning Examine, which seeks to offer perception into regional and interregional grid planning efforts. It predicts a 32% drop in power technology prices by 2030, assuming the completion of vital transmission initiatives.
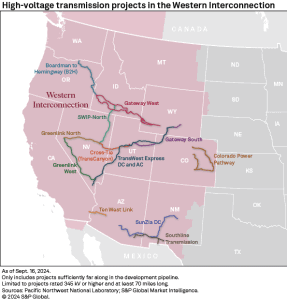
The analysis, led by Konstantinos Oikonomou of PNNL, analyzes how the 12 new transmission strains throughout the Western Interconnection, which can add 3,000 miles of capability, might decrease carbon emissions and improve grid reliability. With this infrastructure, the area might develop its renewable capability by 35 GW of wind, 31 GW of photo voltaic, and 12 GW of power storage.
Within the research, titled the Western Interconnection Baseline StudyPNNL researchers assessed whether or not the present trade planning processes within the West are aligned with nationwide local weather objectives. They created a base case utilizing information from the Western Electrical energy Coordinating Council (WECC). They factored in anticipated generator additions, retirements, new transmission capability, and cargo progress by 2030.
The research then in contrast this base case with a “high renewables case,” which assumes the completion of 12 high-voltage transmission initiatives throughout the area. These initiatives had been chosen as a result of they’re “sufficiently far along in the development pipeline”. Because of this development is both ongoing or in superior phases of federal and state allowing.
Unlocking Renewable Potential
One notable undertaking is the Ten West Hyperlink transmission line, which started business operation in June 2024. Spanning 125 miles, this line is ready to ship over 3 gigawatts (GW) of renewable power to customers in California and the Desert Southwest. Owned by Lotus Infrastructure Companions and operated by California ISO, the Ten West Hyperlink exemplifies the important function transmission strains play in decarbonizing the facility sector.
One other important undertaking within the research is the Gateway West undertaking, which stretches 488 miles and is developed by PacifiCorp. This undertaking is particularly designed to transmit wind power from Wyoming to a substation in Idaho.
From there, the power might be additional transmitted by the Boardman-to-Hemingway transmission line. This almost 300-mile line is a collaborative effort by Berkshire Hathaway Power and different companions.
These interconnected initiatives showcase a coordinated strategy to transferring renewable power from low-density states, like Wyoming and New Mexico, to extra densely populated areas all through the West.
The complementary nature of those initiatives is crucial for guaranteeing that renewable power can stream throughout lengthy distances. This functionality is essential for lowering carbon emissions in massive city facilities, because it permits cities to entry cleaner power sources.
Enhancing Grid Reliability with Excessive Renewables
The transition to renewable energy is crucial for lowering carbon emissions and attaining a sustainable energy grid within the US. Nevertheless, integrating extra renewable sources, like photo voltaic and wind, into the grid presents challenges.
Notably, the PNNL research makes use of a singular modeling strategy referred to as alternating present (AC) energy stream modeling. This methodology differs from the extra conventional manufacturing value evaluation, which primarily focuses on the price of power manufacturing.
As an alternative, AC energy stream modeling permits researchers to simulate how new renewable power sources have an effect on the grid. They’ll determine potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities within the grid when excessive ranges of renewables are built-in.
The research discovered that the extra high-voltage transmission strains would help 29 GW of recent solar capability, 26 GW of onshore wind, 15 GW of battery storageand three GW of offshore wind.
Moreover, the research assumed that each one new photo voltaic installations would incorporate 4-hour battery storage with a storage capability equal to 50% of the photo voltaic useful resource’s nameplate capability. It is a vital function, as it might make photo voltaic and wind power dispatchable. It signifies that power generated by these sources may very well be saved and used when demand spikes or in periods of low technology.
Nevertheless, even with these developments in renewable energy and storagethe research discovered that some thermal technology capability should still be required. That is significantly true through the early morning hours when storage methods will not be absolutely charged or obtainable.
Nader Samaan, a PNNL energy methods analysis engineer and co-author of the research, famous that:
“This could be one of the more challenging periods, where you need to have some thermal generation on your system to help with the morning ramp-up period.”
The completion of the transmission initiatives represents a major step towards attaining a carbon-free energy system within the US West by 2035. The research highlights the significance of advancing transmission infrastructure to help the nation’s decarbonization objectives.