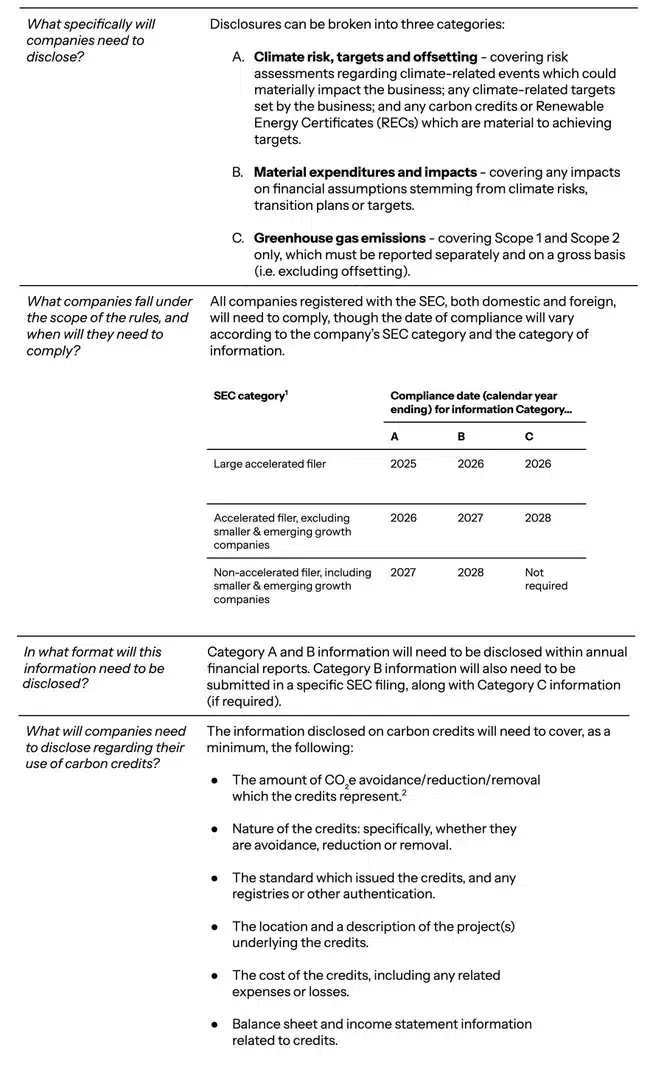
A number of non-public fairness corporations have not too long ago entered the carbon credit score market, capitalizing on the rising demand for high-quality credit. This important market improvement is amid expectations of enhanced transparency from the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)’s new disclosure regulations.
Seizing Alternative Amidst Regulatory Adjustments
The current last guidelines issued by the SEC mandate firms to reveal climate-related data, together with using carbon credits. Whereas the principles symbolize a scaled-back model of the preliminary proposal, notably excluding Scope 3 emissionsthey nonetheless mark a big milestone by requiring lots of the world’s largest companies to reveal their emissions and carbon credit score utilization.
Key gamers on this rising development embody:
- Stafford Capital Companions: the London-based agency goals to lift $1 billion for a fund devoted to investing in forest initiatives to generate round 30 million carbon offsets.
- Bain Capital: the corporate not too long ago supplied backing to Terra Pure Capital, an funding agency specializing in financing offset-generating initiatives like mangrove forest planting and restoration.
- Kimmeridge Power Administration: the New York-based agency pledged as much as $200 million to forest supervisor Chestnut Carbon about two years in the past. Chestnut Carbon focuses on reforestation initiatives.
One facet of the principles that is still ambiguous is the definition of ‘materiality.’ Particularly, firms can undertake a ‘maximum transparency’ method by disclosing all retired carbon credit inside a reporting interval.
Or they could go for a extra selective method by disclosing solely these credit deemed materials to particular climate-related targets. This ambiguity will persist till the primary wave of disclosures underneath the principles is noticed.
SEC Local weather Disclosure Guidelines FAQs
Furthermore, the principles may immediate firms to transcend disclosure and embody climate-related property and liabilities on their steadiness sheets. That is excellent news as a result of it may possibly assist internalize the damaging externalities related to their emissions.
This inner carbon pricing mechanism is anticipated to drive firms to accentuate their efforts in direction of decarbonization inside their worth chains and offset residual emissions by means of buying carbon credit.
From Skepticism to Sustainable Impression
Current analysis by Ecosystem Market’s Forest Developments means that firms buying carbon credit cut back their emissions sooner than their friends. As an example, they’re investing 3x extra in emissions reductions inside their very own worth chains. Analysts see this as an indicator of the potential efficacy of carbon credit score utilization in accelerating local weather motion.
The carbon market is usually met with skepticism as a result of greenwashing claims in opposition to firms taking part in it. As an example, a class-action lawsuit in opposition to Delta Air Lines in California alleged that the service overstated its “carbon neutrality” based mostly on doubtlessly questionable offsets.
Some authorized specialists highlighted a “crisis of confidence” within the high quality of voluntary carbon credits from emission discount initiatives.
In response to those considerations, some corporations, like Bregal Investments in London, have supported builders of carbon-insetting initiatives. These initiatives intention to scale back emissions throughout firms’ provide chains, significantly within the agricultural sector.
In Europe, the place the biggest carbon-trading system exists, new sustainability-reporting guidelines mandate companies to reveal greenhouse fuel emissions throughout their provide chains or by prospects utilizing their merchandise, often known as scope 3 emissions.
Issues in regards to the reliability of carbon credit raised doubts in regards to the effectiveness of those initiatives producing the credit. That is the place the brand new reporting necessities by the SEC would deliver larger transparency to the market.
Shaping the Way forward for Carbon Credit score Buying and selling
The brand new SEC guidelines will topic carbon credit, often known as carbon offsets when used to compensate for an organization’s carbon emissions, to extra scrutiny. Thus, it would drive demand for high-quality offsets.
Within the case of personal fairness corporations, some face authorized challenges and a brief suspension of enforcement by the US appeals court docket. Regardless of this, these companies nonetheless see potential in assembly the unmet demand for high-quality credit with verifiable mitigation advantages.
Final yr noticed a decline within the variety of credit issued to 277, the bottom in 3 years after dropping to 25% year-on-year, in keeping with an MSCI report.
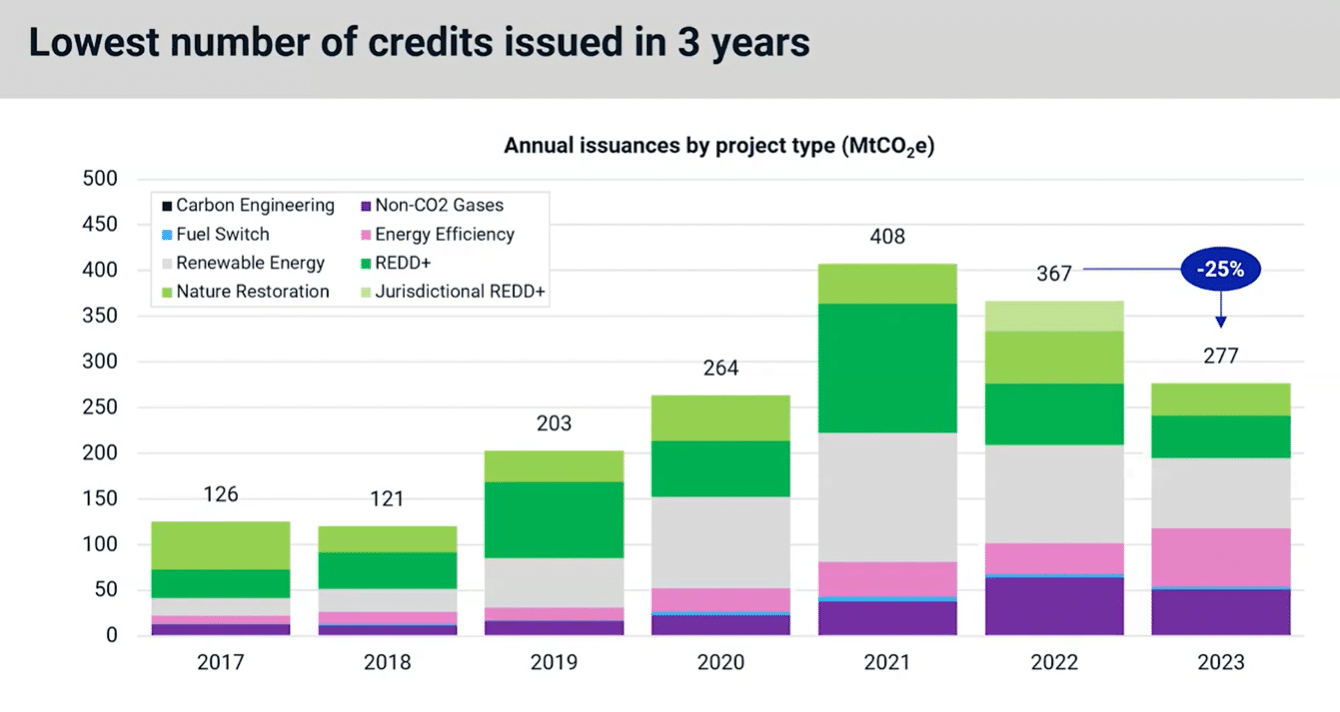
Nevertheless, regardless of the shrinking provide, the common worth dropped by 13% to $6/credit score within the third quarter of 2023. This underscores the necessity for larger transparency and high quality assurance within the carbon credit score market.
Whereas the SEC initially proposed guidelines that require firms to report scope 3 emissions, this provision was dropped from the ultimate model as a result of considerations about compliance prices and issue. Nevertheless, authorized specialists consider that this choice is unlikely to discourage firms from their efforts to scale back scope 3 emissions.
Different jurisdictions, together with California, Illinois, New York, Singapore, and Australia, are additionally adopting or proposing climate-related disclosure guidelines that embody scope 3 emissions.
California, for instance, handed a legislation final yr mandating companies to report each direct and oblique emissions, together with scope 3. Because of this, US public firms should be topic to comparable disclosure necessities from numerous regulators worldwide, regardless of the SEC’s choice.