Credit score: Queensland College of Know-how
A QUT-led crew of worldwide researchers has made a breakthrough within the improvement of a kind of battery that’s a lot safer and cheaper than the batteries at the moment charging our sensible units.
The analysis, published within the Journal of the American Chemical Societyhas demonstrated a means of enhancing the voltage of aqueous zinc-ion batteries, that are a kind of rechargeable battery which have a water-based electrolyte.
QUT researchers concerned within the examine are Professor Ziqi Solar, Affiliate Professor Dongchen Qi, and Fan Zhang from the College of Chemistry and Physics, Professor Ting Liao and Professor Cheng Yan from the College of Mechanical, Medical and Course of Engineering and Dr. Aaron Micallef from the Central Analytical Analysis Facility.
Professor Solar mentioned aqueous batteries had been used for greater than 100 years, primarily as non-rechargeable batteries.
“Improving the low voltage of rechargeable aqueous batteries is one of the biggest hurdles facing their wide-spread implementation for many uses,” Professor Solar mentioned.
“In widespread rechargeable batteries, natural electrolytes are used to fill the area between the anode and cathode, that are costly, and most significantly, extremely flammable.
“The usage of aqueous electrolytes might handle the security difficulty of Lithium-ion batteries, because the aqueous electrolyte is less expensive and safer.
“However using aqueous electrolyte in rechargeable batteries may be very difficult.
“Because of the low reducing voltage of water (1.23V), the aqueous batteries usually have low voltage window and thus low energy density—which means inferior battery performance compared with the normal organic rechargeable batteries.”
Credit score: Journal of the American Chemical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c01188
Fan Zhang, first writer on the analysis paper, mentioned there was an extra problem in growing that 1.23V voltage window with an aqueous electrolyte.
“If the applied voltage is higher than 1.23V, hydrogen will generate and lead to swelling of the battery and possible explosion,” Zhang mentioned.
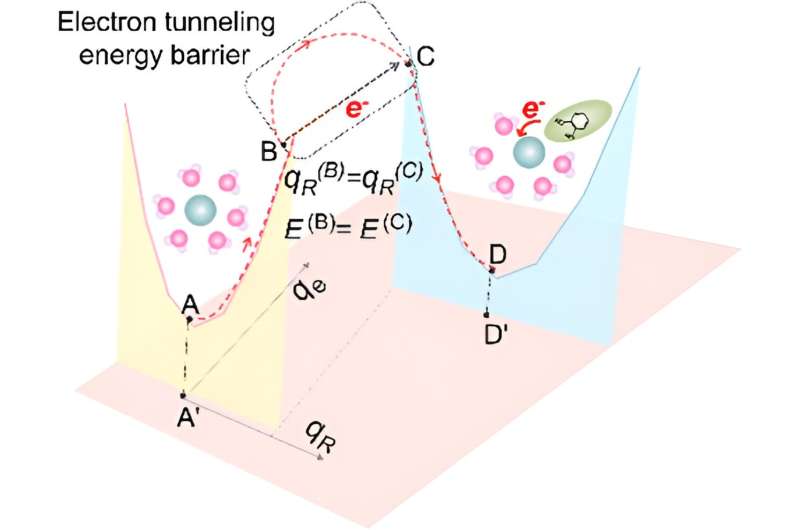
Professor Solar mentioned the researchers discovered a means of accelerating the voltage in a zinc aqueous battery whereas avoiding the doubtless harmful hydrogen build-up. The tactic was impressed by the Marcus Concept for electron switch amongst molecules in an answer, which earned Rudolph Marcus the Nobel Prize.
“In our work, we utilized an natural compound known as catechol into the aqueous zinc sulfate electrolyte, which modifications the electron switch mannequin from a traditional inside sphere switch in electrolyte to an outer sphere switch mannequin.
“In simple terms, this means that catechol compound transfers an electron to the Zinc ion, which results in the water molecules being more stable and the potentially dangerous hydrogen reaction is controlled.”
Professor Solar mentioned the analysis was a step in direction of the growing use of zinc-based aqueous batteries, which have already been proven to have a number of key benefits.
Zinc ions have twice the cost of lithium ions, which suggests twice as a lot vitality. The batteries can be smaller, can cost a lot sooner and have a recharging cycle lifetime of many occasions larger.
“The outer sphere electron transfer mechanism paves us a brand new method to design the high-voltage aqueous electrolytes,” Professor Solar mentioned.
“The usage of this new forms of aqueous electrolyte improves the voltage window for 2 folds larger and enhances the general battery efficiency for 1.5 to a few occasions higher than regular aqueous electrolytes.
“This is a big leap to aqueous rechargeable batteries for industrial production.”
Extra data:
Fan Zhang et al, Outer Sphere Electron Switch Enabling Excessive-Voltage Aqueous Electrolytes, Journal of the American Chemical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c01188
Offered by
Queensland University of Technology
Quotation:
Analysis crew improves voltage of aqueous rechargeable batteries within the quest for safer, cheaper choices (2024, April 30)
retrieved 30 April 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-04-team-voltage-aqueous-rechargeable-batteries.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
