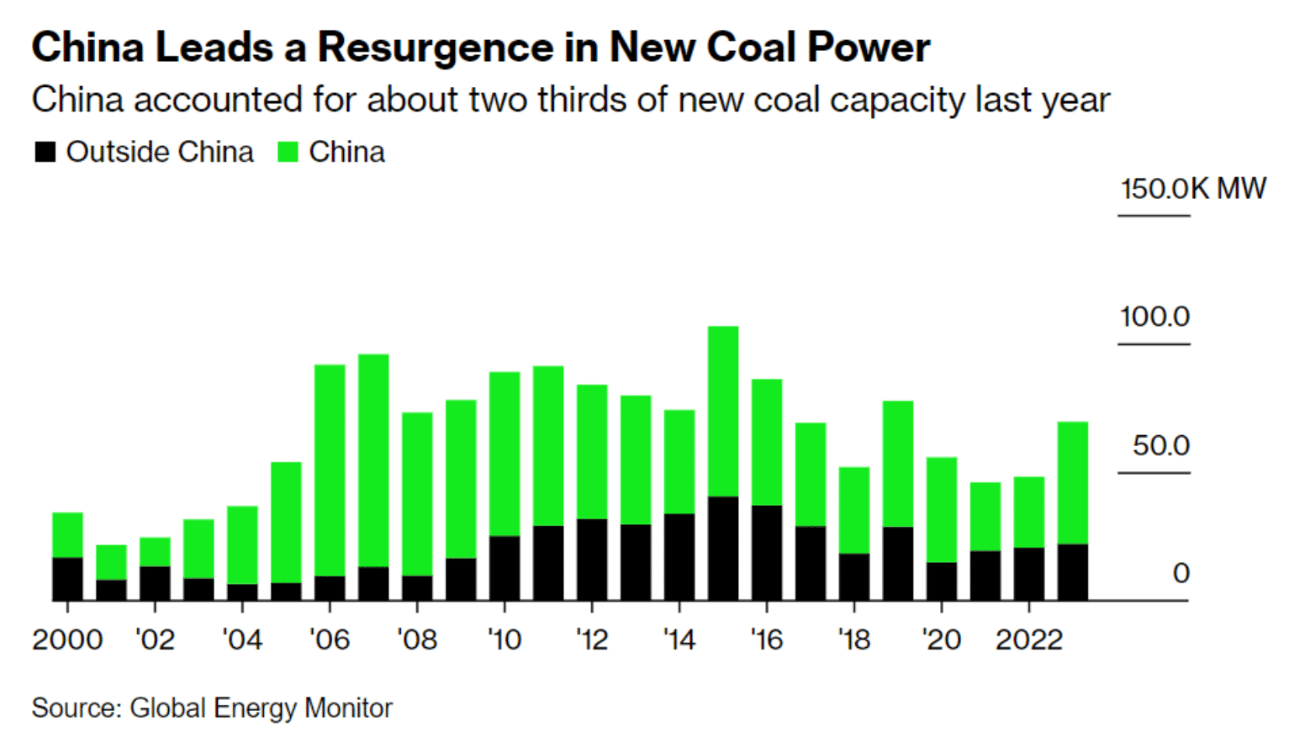
In a major growth for the worldwide power panorama, China has led a surge in coal-power capability, driving the world’s whole to a file excessive in 2020, in keeping with a brand new report from International Power Monitor. This enhance was primarily fueled by new crops in China, which accounted for about two-thirds of the enlargement, with Indonesia and India following carefully behind.
The Present State of Coal Consumption
The coal fleet expanded by 2% to 2,130 gigawatts, a exceptional enhance pushed by a lower in retirements worldwide. This pattern was notably distinguished in China, the place the nation initiated the development of 70 gigawatts of recent coal crops in 2020. That’s almost 20x greater than the remainder of the world mixed.
The reporttitled “Global Coal Plant Tracker 2021: The World’s 1000 Largest Coal Plants,” highlights the numerous function China performs within the world coal market.
The nation’s aggressive enlargement of coal-power capability is a stark distinction to the pattern of retiring coal crops in lots of developed nations, similar to america and the European Union.
The rise in coal-power capability has vital implications for world power markets and local weather coverage initiatives.
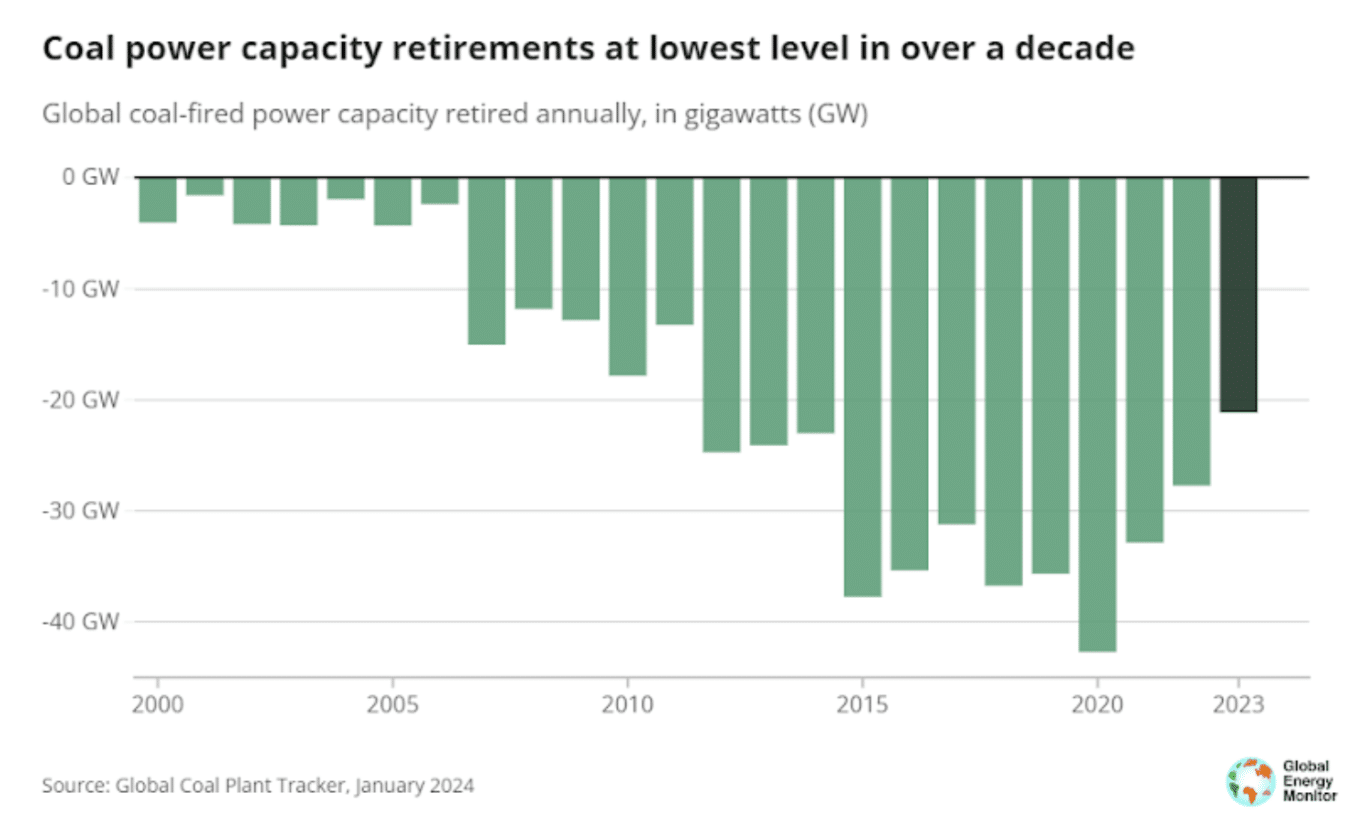
In accordance with International Power Monitor, about as many nations opened new coal plant items as shut items down in 2023. But general, extra capability is added than retired.
Listed here are 8 key factors from the coal report:
- International working coal capability grew by 2% in 2023with China driving two-thirds of recent additions. Nevertheless, this accelerated development in coal capability could also be short-lived, as low retirement charges in 2023 that contributed to coal’s rise are anticipated to select up pace within the U.S. and Europeoffsetting the blip.
- Heightened capability additions will even be tempered if China takes instant motion to make sure it meets its goal of shutting down 30 gigawatts (GW) of coal capability by 2025. International locations with coal crops to retire want to take action extra rapidly, and nations with plans for brand spanking new coal crops should guarantee these are by no means constructed.
- In any other case, assembly the objectives of the Paris Settlement and reaping the advantages of a swift transition to wash power will likely be tough. Coal’s fortunes this 12 months are an anomaly, as all indicators level to reversing course from this accelerated enlargement.
RELEVANT: Global Team Develops World’s First “Coal-to-Clean” Carbon Credit Program
- The information for the report comes from GEM’s International Coal Plant Tracker, a web based database up to date biannually that identifies and maps each recognized coal-fired producing unit and each new unit proposed since January 1, 2010 (30 MW and bigger). This knowledge serves as an important worldwide reference level utilized by organizations together with the IPCC, IEA, and the UN.
- In accordance with the IEA, world coal demand is predicted to say no by 2.3% in 2026 in comparison with 2023 ranges. And that’s even with out stronger clear power and local weather insurance policies. This decline is pushed by the key enlargement of renewable power capability coming on-line within the three years to 2026.
- Greater than half of the worldwide renewable capacity enlargement is about to happen in China, which at present accounts for over half of the world’s demand for coal. In consequence, Chinese language coal demand is predicted to fall in 2024 and plateau by 2026.
- The shift in coal demand and manufacturing to Asia is accelerating, with China, India, and Southeast Asia set to account for three-quarters of world consumption in 2023, up from solely about one-quarter in 1990. Consumption in Southeast Asia is predicted to exceed that of the U.S. and the EU in 2023.
- The three largest coal producers globally – Indonesia, China, and India – are anticipated to break production records in 2023, pushing world output to a brand new excessive. Nevertheless, to lower emissions at a charge preserving with Paris Settlement objectives, relentless coal use would wish to fall far more rapidly.
China’s Pivotal Function and the Shift in Coal’s International Management
China’s development in coal capability highlights its give attention to fulfilling power wants for financial and industrial enlargement, regardless of world efforts to chop greenhouse fuel emissions. The interaction between growing coal capability and the shift towards cleaner power will considerably affect the worldwide power situation.
The function of China and different key gamers on this course of will likely be essential in figuring out the tempo and scope of the shift in the direction of a extra sustainable power future.
The report additional highlights a major shift in world management concerning coal insurance policies, notably throughout the G7 and G20 nations. The G7 nations, which accounted for 23% of the world’s working coal capability in 2015, have diminished their share to fifteen% in 2023.
The discount is underscored by the completion of recent items in Japan. This marks the top of coal building throughout the G7, though proposals nonetheless exist in Japan and the U.S.
In the meantime, the G20 nations maintain 92% of the world’s working coal capability, with Brazil, the present G20 chair, witnessing a lower in pre-construction capability, leaving solely two tasks remaining in Latin America.
This geographical shift in coal insurance policies and tasks underscores a broader world pattern towards decreasing reliance on coal. Furthermore, it would have vital implications for international energy markets and local weather coverage initiatives.
Coal Plant Proposals and Retirements
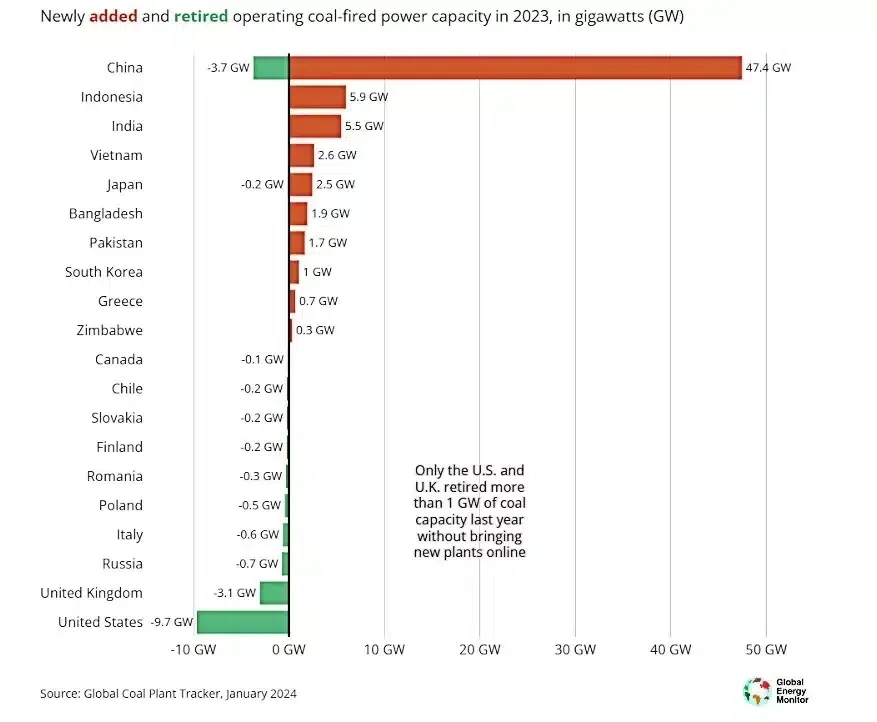
The dynamics of coal plant proposals and retirements present a nuanced view of the worldwide coal trade’s future. In 2023, whereas 69.5 GW of coal energy capability was added, solely 21.1 GW was retired, resulting in a web enhance in world coal capability.
This pattern is especially pronounced exterior of China, the place new proposals totaled 20.9 GW, led by nations like India, Kazakhstan, and Indonesia.
Regardless of a normal pattern towards decommissioning, these developments point out a fancy world panorama the place sure regions continue to explore new coal projects.
This ongoing exercise means that whereas the worldwide momentum is in the direction of decreasing coal dependency, attaining this aim requires concerted efforts throughout all nations, notably these with vital new proposals.