Researchers from IIT Madras have found that the Indian Ocean may very well be a promising website for storing huge quantities of carbon dioxide completely. They suggest CO2 storage in liquid swimming pools or strong hydrates at sure depths, which they imagine gained’t hurt the marine ecosystems. This technique may help India in decarbonizing its industrial hubs and reaching its 2070 net-zero target.
Unlocking the Analysis Insights of the Indian Ocean’s CO2 Storage Potential
Many famend oceanographers have famous that, amongst all of the world’s oceans, the Indian Ocean is presumably probably the most under-researched. CCS entails capturing CO2 emissions from industrial sources or the ambiance and storing them deep underground or in oceanic reservoirs.
Presently, IIT-Madras is exploring the carbon sequestration capability of this ocean basin. Listed here are the important thing factors from their findings:
CO2 Storage Capability
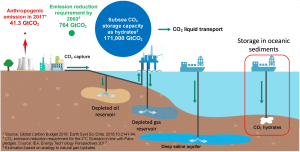
Researchers have estimated that the Bay of Bengal, the northeastern a part of the Indian Ocean may alone sequester a number of hundred gigatons of anthropogenic CO2 in ocean and marine sediments. This amount is the same as the whole greenhouse fuel emissions produced by India over a number of years.
CO2 Storage Varieties
The analysis findings additional state that saved CO2 can exist in two kinds:
Fuel Hydrates: Past a sure depth (deeper than 500 meters), the saved CO2 can type an environmentally pleasant ice-like substance generally known as “gas hydrates”. Below oceanic circumstances, roughly 150-170 cubic meters of CO2 could be sequestered by one cubic meter of fuel hydrate.
Liquid Swimming pools and Stable Hydrates: At depths exceeding 2800 meters, CO2 could be completely saved as liquid swimming pools and strong hydrates. As soon as transformed into fuel hydrate, CO2 can not escape into the ambiance as a consequence of gravitational and hydrate permeability boundaries inside the subsea sediments.
Professor Jitendra Sangwai, Dept of Chemical Engineering, IIT Madras spearheading the analysis has recognized the muse of the research. He mentioned,
“Methane hydrate have been in the ocean for millions of years without affecting the environment. Methane is more potent GHG than CO2. This attracts researchers to explore the ocean to store CO2 permanently.”
IIT Madras’ analysis gives essential insights into optimizing CO2 storage methods. By analyzing elements comparable to clay focus, additive properties, and native ocean ground traits, researchers can establish probably the most environment friendly strategies for subsea CO2 sequestration.
This pioneering analysis from IIT Madras affords vital promise for India’s efforts in opposition to local weather change. By leveraging the Indian Ocean and Bay of Bengal’s CO2 storage potential, India can take strides in direction of its decarbonization objectives and pave the way in which for a extra sustainable future.
An identical research was performed on the Nationwide College of Singapore. The analysis group at NUS mentioned that this expertise has the potential to evolve right into a commercial-scale course of. It may allow international locations like Singapore to effectively sequester greater than 2MTs of CO2 yearly as hydrates to fulfill emission discount targets.
This picture will outline the method of storing CO2 in oceans.
Guaranteeing the Security of the Marine Ecosystem
Whereas utilizing the ocean as a CO2 storage sink is engaging, direct storage at shallow depths may hurt marine life. Due to this fact, they should retailer the CO2 completely within the ocean at particular depths or at sub-sea sediments to keep away from ecological harm to the Indian Ocean, Bay of Bengal, and surrounding coastal areas.
Mr. Yogendra Kumar Mishra, a analysis scholar at IIT Madras has identified,
“There are various methods for CO2 sequestration,” mentioned “While the ocean presents a viable storage solution, directly injecting CO2 into shallow waters can harm marine life. Our research explores permanent storage options at greater depths.”
Oceanic Carbon Seize Bolstering India’s Pledge to Web Zero
Nevertheless, India is searching for a long-term and large-scale CO2 sequestration expertise to decarbonize heavy industries like energy, metal, and transport. Oceanic CO2 seize has huge potential to transition towards carbon neutrality.
Wanting again, Europe tailored this strategy to retailer CO2 within the North Sea. Northern European international locations like Denmark and Norway are actively implementing carbon sequestration initiatives within the North Sea. These applications contain capturing CO2 and storing it in outdated oil and fuel reservoirs or saline aquifers beneath the seabed. Most CCS applications are ruled by the legal guidelines of the internet hosting nation, regardless of some efforts towards worldwide cooperation.
Equally, the Indian Ocean and the Bay of Bengal supply huge expanses the place captured CO2 could be safely saved, probably mitigating the impacts of local weather change.
As governments decide to reaching net-zero carbon emissions by 2050, they’re addressing the problem of managing residual CO2 emissions, notably from heavy industries.
India’s pursuit of CCS expertise for ocean CO2 seize aligns with its broader local weather objectives. It contains the nation’s dedication to realize net-zero emissions by 2070.
By investing in CCS initiatives’ analysis, growth, and implementation, India goals to shrink its carbon footprint and contribute to international local weather change.
In abstract, this analysis gives a promising avenue for addressing local weather change by leveraging the huge potential of the Indian Ocean’s CO2 storage and sequestration.