The significance of local weather finance in driving inexperienced investments has by no means been extra pronounced as highlighted by Avangrid’s True North photo voltaic challenge in Falls County, Texas. The challenge, benefiting from subsidies beneath the Inflation Discount Act, displays a rising development in the direction of climate-friendly initiatives supported by authorities incentives.
Nevertheless, assembly international local weather objectives requires vital scaling up of investments in renewable power, power effectivity, and ecosystem restoration. The Worldwide Renewable Power Company estimates that a median of 11,000 gigawatts of renewable power capacity must be constructed yearly till 2030, calling for substantial monetary commitments.
Bridging the Local weather Funding Hole
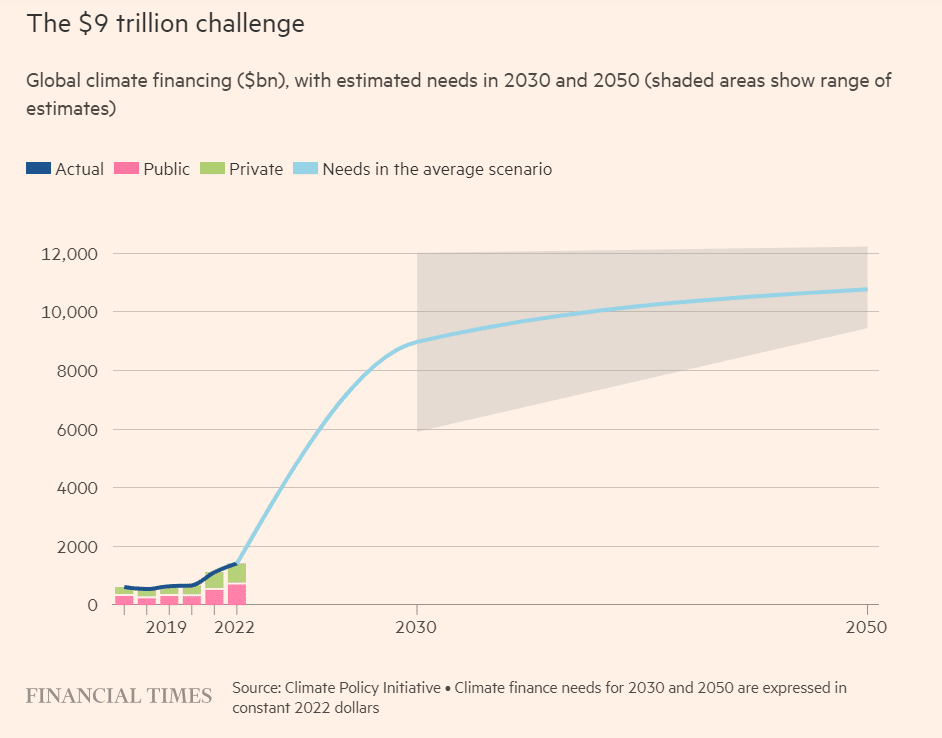
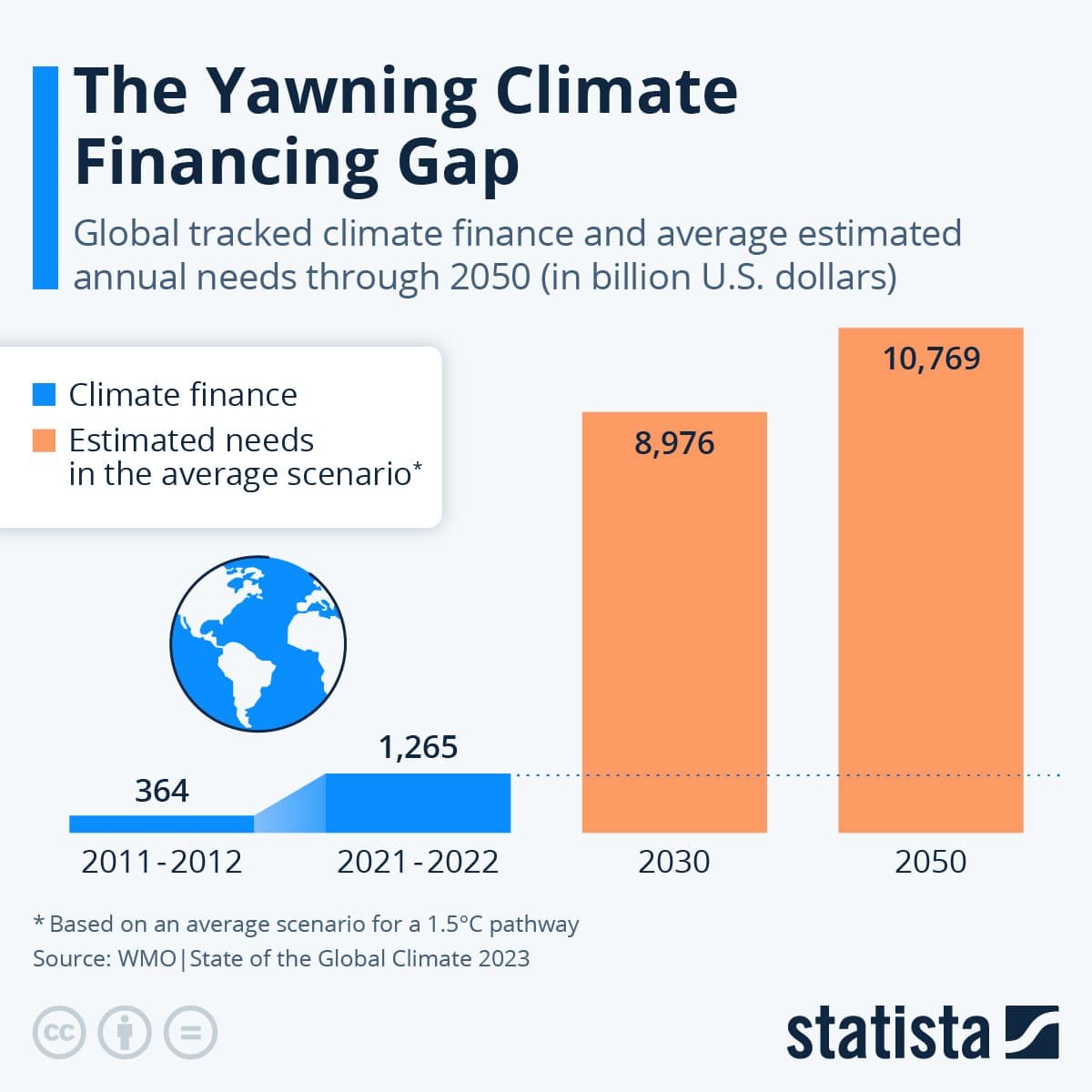
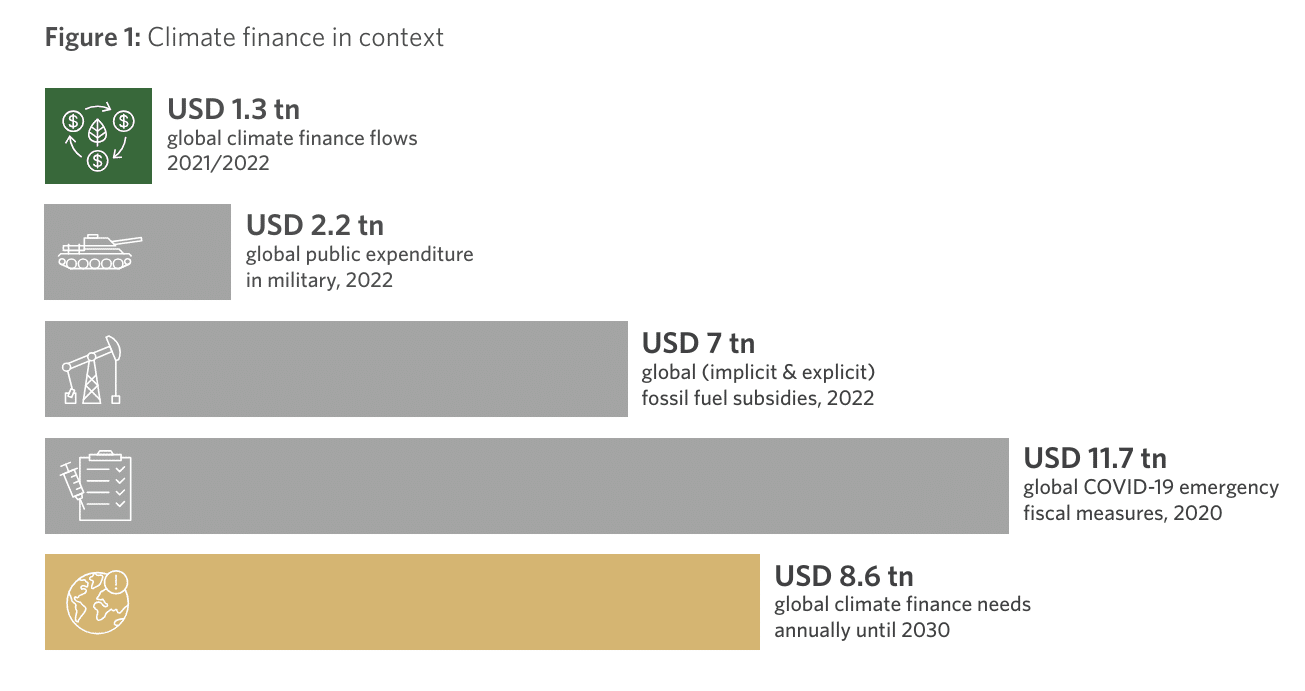
In accordance with the Local weather Coverage Initiativeinternational local weather finance wants to extend to about $9 trillion yearly by 2030 to restrict common international temperature rises according to the Paris Settlement. Europe alone requires €800 billion in power infrastructure funding to satisfy its 2030 local weather targets. The area wants a complete of €2.5 trillion wanted for the green transition by 2050.
In 2021-22, local weather financing reached virtually $1.3 trillion, a big enhance from $364 billion in 2011-12. Most of this progress is attributed to mitigation finance, notably in renewable energy and transport sectors. Notable will increase are in clear power investments in China, the USA, Europe, Brazil, Japan, and India.
Nevertheless, adaptation finance lags behind, reaching solely $63 billion in 2021-22. That is removed from the estimated $212 billion wanted by creating nations alone by 2030. Adaptation finance goals to boost communities’ resilience to local weather hazards, however funding falls quick.
Analysts estimate that the $9 trillion has to rise to over $10 trillion yearly from 2031 to 2050.
To deal with this financing hole, governments are exploring numerous mechanisms, together with wealth taxes, levies on transport, and company taxes. For example, the US plans to lift $300 billion over a decade by way of a minimal tax on company earnings and a inventory buyback tax to fund local weather initiatives.
Ramping Up Local weather Finance
The urgency of local weather finance has been underscored by worldwide commitments to section out fossil fuels and triple renewable power capability by 2030.
The upcoming COP29 convention in Baku, Azerbaijan, is predicted to focus extensively on local weather finance, notably establishing international objectives to assist creating nations’ transition efforts.
The non-public sector has a big function in financing the inexperienced transition (70%), however the public sector should additionally contribute. The Worldwide Power Company means that public finance might want to cowl about 30% of worldwide local weather finance. Public funds ought to primarily concentrate on crucial infrastructure and adaptation measures.
Governments are exploring numerous revenue-raising choices, together with carbon pricing mechanisms and taxes on fossil gas extraction. Eire’s carbon taxfor instance, allocates elevated revenues to climate-related investments and gas poverty prevention.
Different nations are contemplating modern financing approaches, comparable to windfall taxes on oil and fuel firms and tourism taxes. Moreover, efforts are underway to section out fossil gas subsidies, redirecting funds in the direction of local weather motion initiatives.
Navigating the Local weather Financing Maze
Regardless of the financing challenges, power strategist Kingsmill Bond argues that capital is obtainable however have to be deployed successfully. Clever regulation and incentives just like the EU’s REPowerEU technique can mobilize non-public investments in renewables and drive sustainable progress.
In creating nations, the place monetary constraints are extra pronounced, worldwide cooperation and concessional financing are essential. Sovereign inexperienced bonds and local weather finance frameworks goal to mobilize non-public sector funding and assist inexperienced tasks in rising economies.
The authors of the CPI’s Global Landscape of Climate Finance 2023 report counsel that closing the funding hole is theoretically possible, notably given international spending developments. They level out that whereas international navy spending reached $2.2 trillion in 2022 (SIPRI, 2023), emergency fiscal measures totaling $11.7 trillion had been introduced globally in response to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, in keeping with the Worldwide Financial Fund.
Shifting ahead, the CPI recommends addressing inequalities in present local weather finance distribution. Regardless of agriculture and trade being vital emission sources, they obtained disproportionately low funding in 2021-22 relative to their mitigation potential. The report additionally emphasizes the significance of investing in rising applied sciences like battery storage and hydrogenhighlighting untapped funding alternatives.
Finally, attaining a sustainable and resilient future requires concerted efforts from governments, companies, and monetary establishments. By shifting monetary sources in the direction of climate-friendly investments, the worldwide neighborhood can speed up the transition to a greener economic system and mitigate the impacts of local weather change.