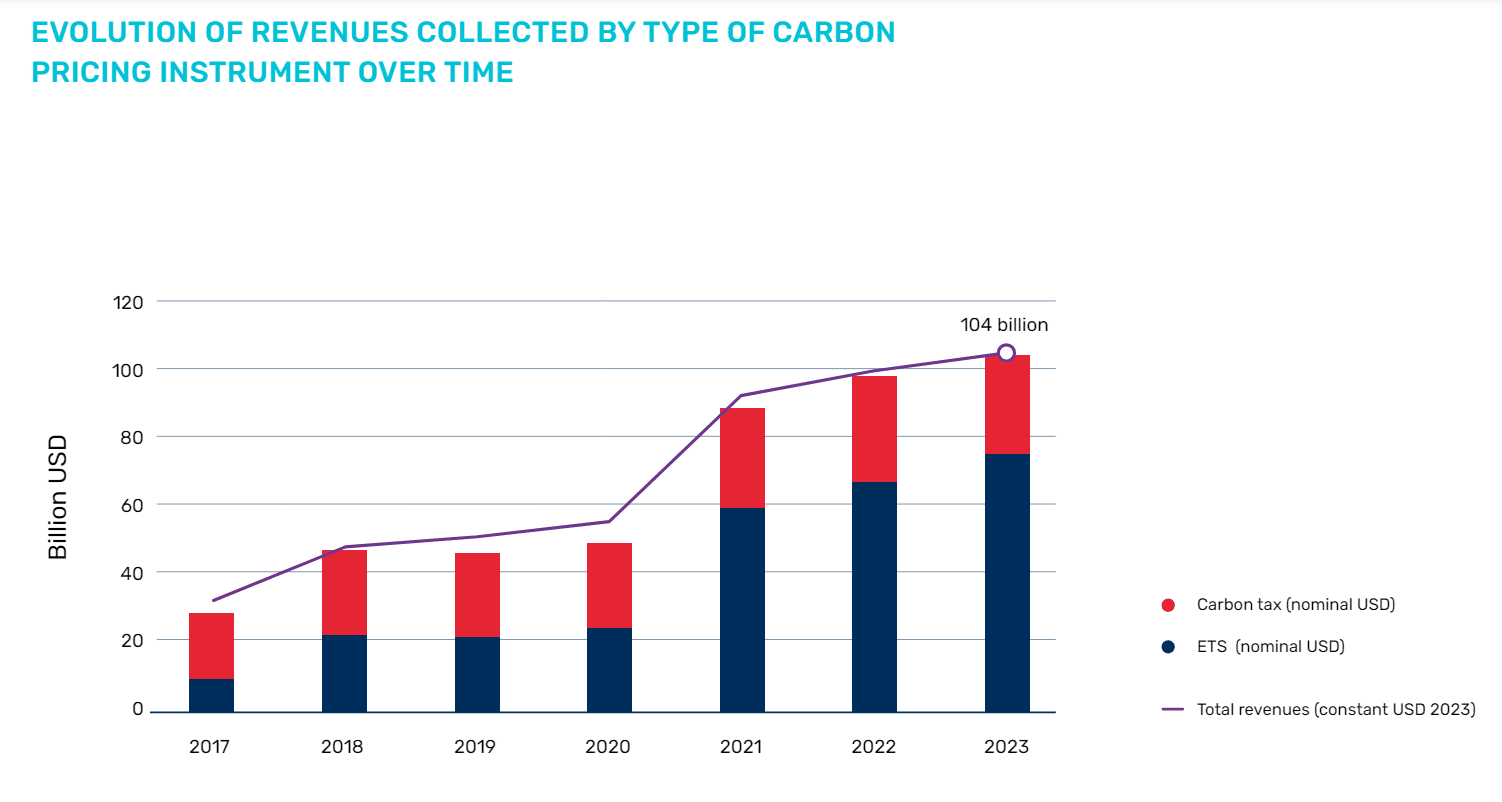
A World Financial institution report reveals that nations with carbon pricing mechanisms generated a file $104 billion in revenues final 12 months. Over half of the funds had been directed in the direction of local weather and nature-related packages.
Carbon pricingcarried out by carbon taxes or emissions buying and selling programs (ETS), is essential for decreasing emissions and fostering low-emission progress.
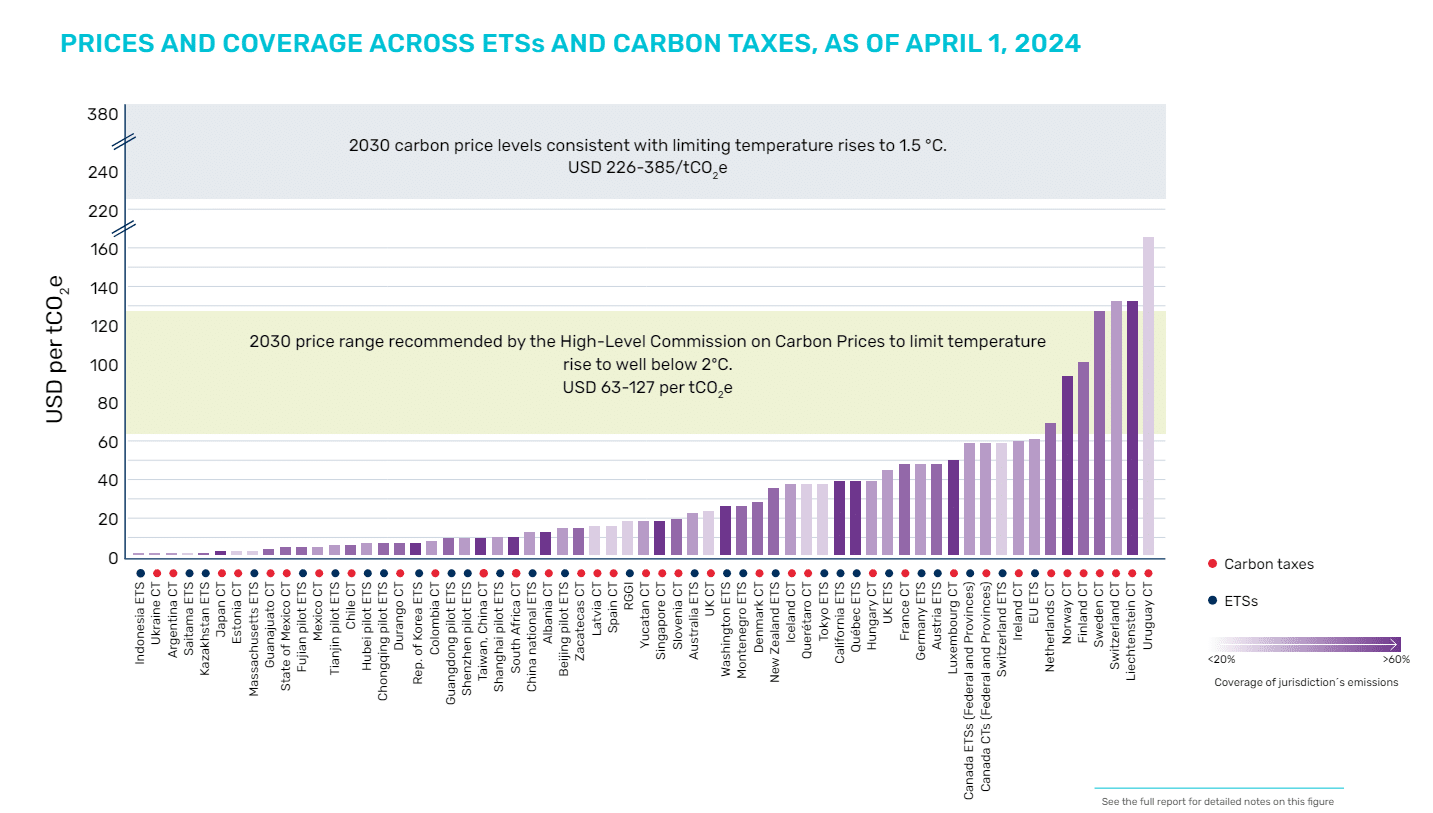
Regardless of this achievement, the report emphasizes that present carbon taxes and emissions trading schemes stay inadequate to fulfill the Paris Settlement’s local weather objectives. Though 24% of worldwide emissions are lined by some type of carbon pricing, lower than 1% are topic to costs excessive sufficient to restrict temperature will increase to beneath 2°C.
The Excessive-Stage Fee on Carbon Costs beneficial carbon prices be within the $50-100 per ton vary by 2030. Adjusted for inflation, this vary is now $63-127 per ton.
The World Financial institution stresses the necessity for elevated protection and better pricing to drive vital reductions in international emissions and help the transition to a low-carbon financial system. Listed below are the important thing takeaways from the WB’s “State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2024.”
Rising Uptake of Center-Revenue Nations However Carbon Costs Stay Inadequate
Over the previous 12 months, the adoption of carbon pricing has been restricted, however there are promising indicators of uptake in middle-income nations.
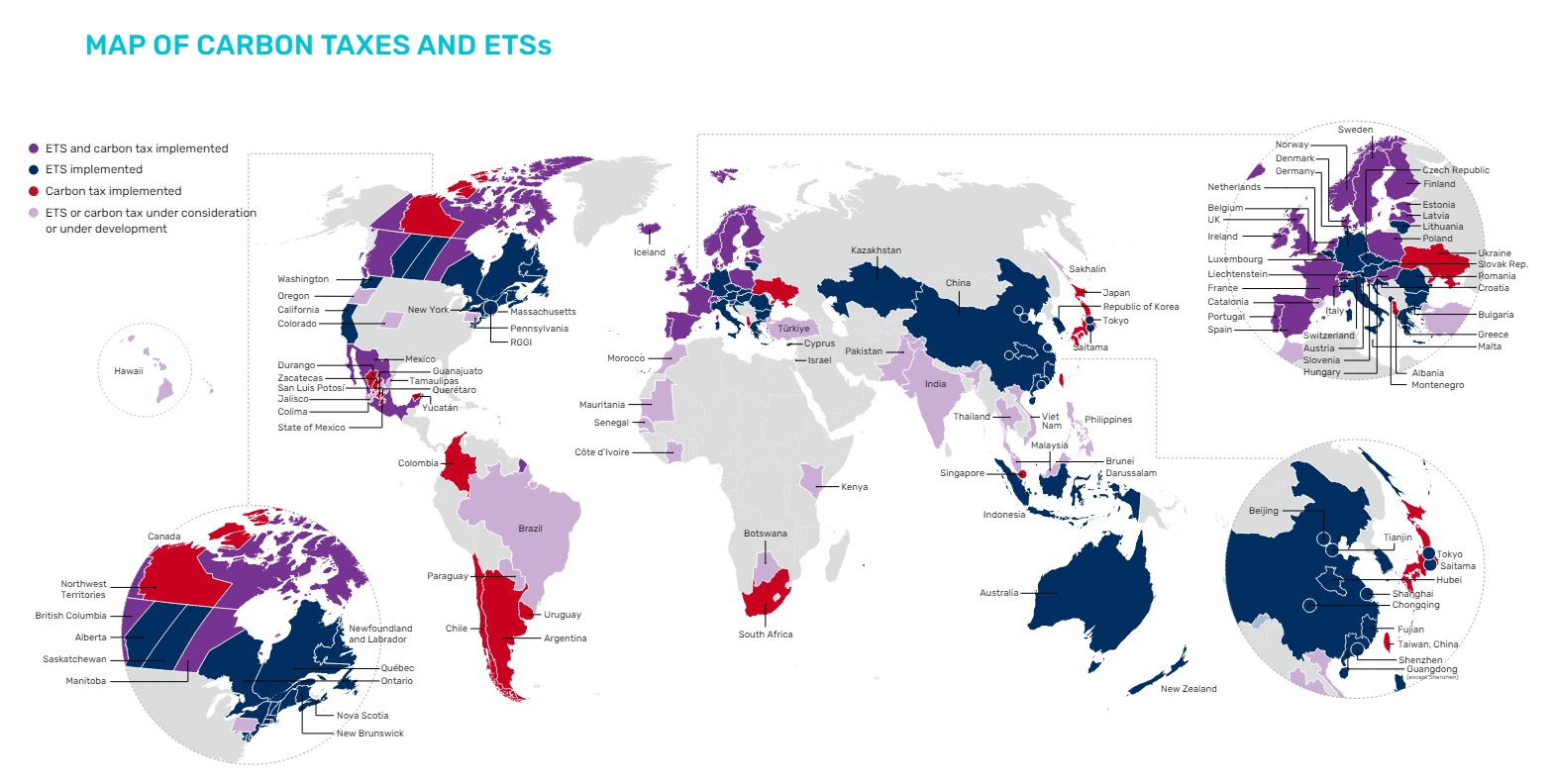
Presently, there are 75 carbon taxes and emissions buying and selling schemes in operation worldwide, reflecting a web acquire of two carbon pricing devices over the previous 12 months. Notably, middle-income nations comparable to Brazil, India, and Turkey have made vital progress in the direction of implementing carbon pricing mechanisms.
Progress has additionally been seen on the subnational stage, regardless of some setbacks. Moreover, sector-specific multilateral initiatives for worldwide aviation and transport have superior.
These developments point out a rising international dedication to addressing local weather change by financial incentives.
Regardless of a decade of robust progress, carbon costs stay inadequate. There exists a notable implementation hole between nations’ commitments and the insurance policies they’ve put into place.
Presently, carbon pricing devices cowl round 24% of worldwide emissions. Whereas the consideration of latest carbon taxes and emissions buying and selling programs (ETSs) may probably enhance this protection to virtually 30%, reaching this may require robust political dedication.
Over the previous 12 months, carbon tax charges have seen slight will increase; nonetheless, worth adjustments inside ETSs have been combined, with 10 programs experiencing worth decreases, together with long-standing ETSs within the European Union, New Zealand, and the Republic of Korea. In consequence, present worth ranges proceed to fall in need of the ambition wanted to realize the objectives of the Paris Settlement.
Carbon Pricing Hit New Highs
In 2023, carbon pricing revenues reached new highs, exceeding USD 100 billion for the primary time. This milestone was pushed by excessive costs within the EU and a brief shift in some German ETS revenues from 2022 to 2023.
ETS continued to account for almost all of those revenues. Notably, over half of the collected income was allotted to funding climate- and nature-related packages. Regardless of this record-breaking income, the general contribution of carbon pricing to nationwide budgets stays low.
On a optimistic observe, rising versatile designs and approaches mirror the adaptability of carbon pricing to nationwide circumstances.
Governments are more and more using a number of carbon pricing instruments in parallel to develop each protection and worth ranges. Whereas carbon pricing has historically been utilized within the energy and industrial sectors, it’s now being more and more thought of for different sectors comparable to maritime transport and waste administration.
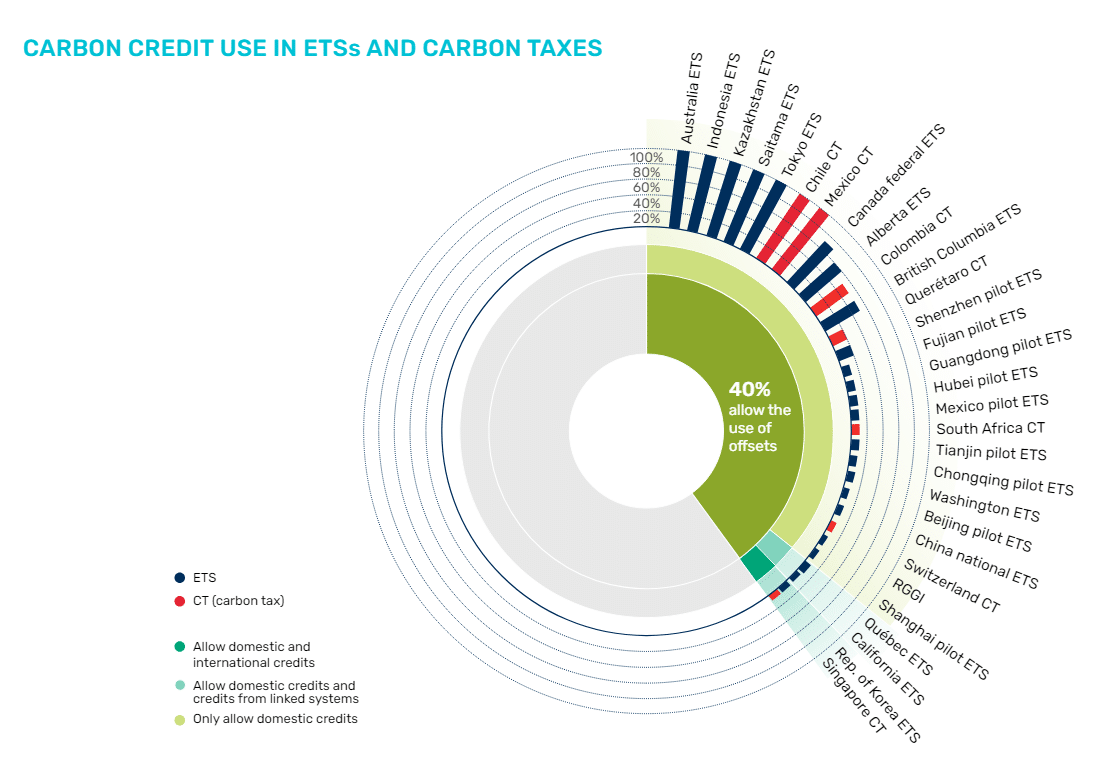
Moreover, governments proceed to allow regulated entities to make use of carbon credit to offset carbon pricing liabilitiesenhancing flexibility, decreasing compliance prices, and lengthening the carbon price sign to uncovered sectors. Past mitigation, carbon pricing additionally gives vital fiscal advantages, additional demonstrating its multifaceted benefits.
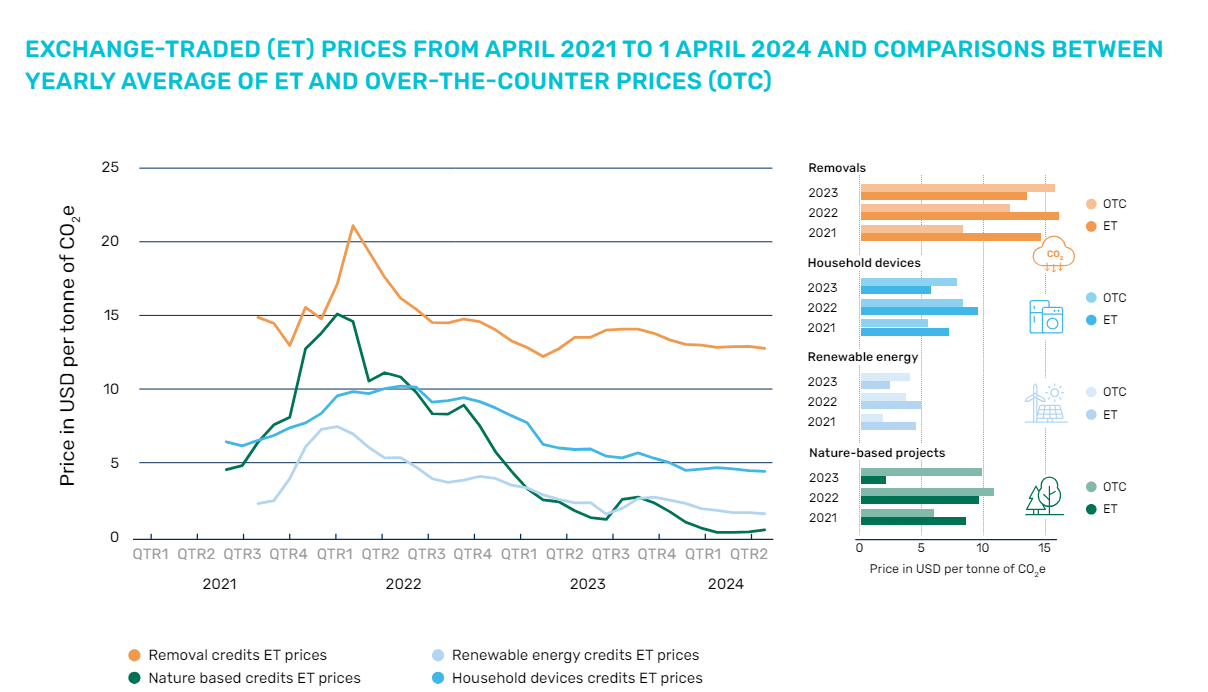
Carbon Credit score Markets Noticed Combined Actions: ET vs. OTC
Governments, notably in middle-income nations, are more and more incorporating crediting frameworks into their coverage to help each compliance and voluntary carbon markets. Regardless of this, credit score issuances fell for the second consecutive 12 months, and retirements remained considerably beneath issuances, leading to a rising pool of non-retired credit out there.
Whereas compliance demand is constructing, voluntary demand continues to dominate. Costs declined throughout most mission classes, excluding carbon removing tasks, which noticed elevated curiosity.
Costs additionally proved extra resilient in over-the-counter transactions, the place consumers can pursue particular buying methods. Credit with particular attributes—comparable to co-benefits, corresponding changes, or latest vintages—traded at a premium, highlighting the extra worth these traits provide to consumers.
Restoring the Integrity of Carbon Credit
The subdued market and lowered confidence underscore the significance of initiatives geared toward rebuilding the integrity and credibility of carbon credit. The integrity of those credit stays a essential concern for the market.
To handle this, the Integrity Council for the Voluntary Carbon Market has established a benchmark for credit score high quality, with the primary tranche of accepted credit anticipated in 2024. On the demand facet, efforts have been directed in the direction of emphasizing the discount of operational and worth chain emissions and exploring the potential position of carbon credit in addressing residual emissions.
Moreover, the event and implementation of Paris Settlement Article 6 continues, regardless of dealing with setbacks and delays. These efforts are important to restoring confidence and making certain the effectiveness of carbon credit score markets.