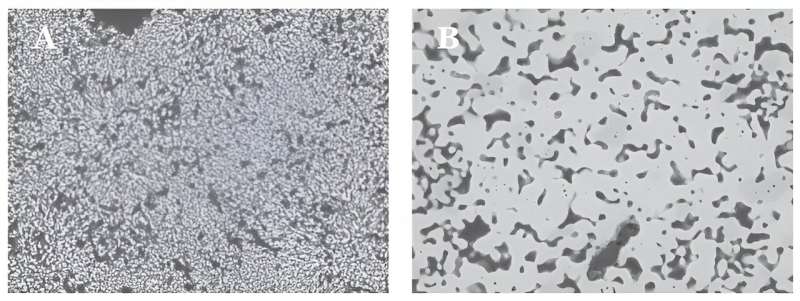
The microstructure of quicklime calcined in a high-CO2 environment (75 x 100 µm) at (A) 1100℃ and (B) 1350℃. Credit score: https://umu.diva-portal.org/smash/report.jsf?pid=diva2percent3A1855537&dswid=5100
The manufacturing of cement and quicklime is power demanding and causes excessive carbon dioxide emissions. It’s because the gas, which is used for heating, and the limestone, which is transformed into quicklime at excessive temperatures, emits carbon dioxide. By changing fossil fuels with renewable ones, emissions might be decreased by as much as 40%.
“A shift from coal to biomass can affect product quality, through reactions at high temperatures,” says Karin Sandström, doctoral scholar. Sandström defends her doctoral thesis on Might 31.
The manufacturing of quicklime and cement takes place in direct-fired kilns, which signifies that the gas, uncooked materials and product are in direct contact with one another. The ash fashioned after combustion can react with the product. For quicklime, which requires a excessive calcium oxide content material, this may have a unfavorable impact on the product high quality.
In laboratory research, Sandström, doctoral scholar on the Division of Utilized Physics and Electronics and the Industrial Doctoral Faculty at Umeå College, and her colleagues have seen that the microstructure of quicklime alters when the limestone is uncovered to ash from biofuels at excessive temperatures. They’ve additionally investigated how impurities present in limestone quarries have an effect on the standard of the quicklime product.
The volatilization of hint and minor parts throughout cement clinker formation was studied each in a standard combustion environment and in an environment with a excessive carbon dioxide content material, comparable to electrified heating.
“For the vast majority of elements, no difference between the two atmospheres was determined. However, a high carbon dioxide content reduced the evaporation of potassium, sodium, and sulfur, which can affect the cement quality. This should be further studied,” says Sandström.
Sandström’s analysis has contributed to an elevated understanding of how impurities, both launched by way of biomass or uncooked materials, have an effect on the product quality in quicklime manufacturing—and the way electrified heating impacts cement high quality. This information is essential within the transition to extra sustainable cement and quicklime manufacturing.
“Future studies can bridge the gap between lab-scale experiments and large-scale processes, with the long-term goal of achieving efficient and sustainable production of cement and quicklime with reduced carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere,” says Sandström.
Extra data:
Results of impurities on section equilibrium in quicklime and cement clinker manufacturing. umu.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A1855537&dswid=5100
Offered by
Umea University
Quotation:
New analysis reveals how biofuels have an effect on cement manufacturing (2024, Might 23)
retrieved 23 Might 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-05-biofuels-affect-cement-production.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.