These novel methods will help within the improvement of perovskites for sustainable vitality and catalysis applied sciences. Credit score: Tokyo Institute of Know-how
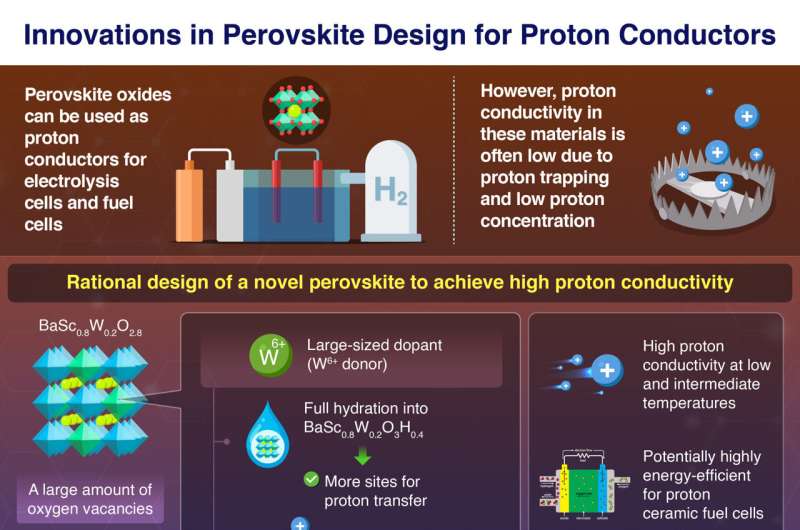
As a newly developed perovskite with a considerable amount of intrinsic oxygen vacancies, BaSc0.8W0.2O2.8 achieves excessive proton conduction at low and intermediate temperatures, report scientists at Tokyo Tech.
By the donor doping of huge W6+this materials can take up extra water to extend its proton focus, in addition to cut back the proton trapping by electrostatic repulsion between the dopant and proton. These findings might pave the best way for the rational design of novel perovskites for protonic ceramic gas cells (PCFCs) and electrolysis cells (PCECs).
In step with world efforts in direction of cleaner vitality applied sciences, gas cells could quickly change into an indispensable instrument for changing chemical vitality—saved within the type of hydrogen or different fuels—into electrical vitality. Among the many varied sorts of gas cells being actively researched, those who use stable electrolytes somewhat than liquid ones have inherent security and stability benefits.
Particularly, protonic ceramic gas cells (PCFCs) have attracted particular consideration amongst scientists. These gadgets don’t function through the conduction of oxide ions (O2−) however mild protons (H+) with smaller valence. A key function of PCFCs is their capacity to operate at low and intermediate temperatures within the vary of fifty–500 °C. Nonetheless, PCFCs based mostly on perovskite electrolytes reported to this point undergo from low proton conductivity at low and intermediate temperatures.
In a latest examine, a analysis staff led by Professor Masamoto Yashima from Tokyo Institute of Know-how (Tokyo Tech), in collaboration with Excessive Vitality Accelerator Analysis Group (KEK), has got down to handle this limitation of perovskite-based proton conductors. Their findings were published within the Journal of Supplies Chemistry A on Could 3, 2024.
However why is the conductivity of the traditional perovskite-type proton conductors so low? “A major problem with the conventional proton conductors is a phenomenon known as proton trapping, in which protons are trapped by acceptor dopant via electrostatic attraction between the dopant and proton,” explains Yashima. “Another major problem among such proton conductors would also be their low proton concentration due to the small amount of oxygen vacancies.”
To sort out these points, the researchers developed a extremely oxygen-deficient perovskite, particularly BaScO2.5 doped with W6+ cations, or BaSc0.8W0.2O2.8 . Because of its giant quantities of oxygen vacancies, this materials has the next proton focus than different proton-conducting perovskites. Nonetheless, since proton hopping happens between oxygen atoms, the oxygen vacancies would decrease proton conductivity somewhat than enhance it.
This downside was solved by full hydration of the perovskite, turning it into BaSc0.8W0.2O3H0.4. Due to the big measurement of the W6+ dopant, the perovskite has a bigger lattice quantity, which suggests it may possibly take up extra water molecules than these doped with different cations equivalent to small Mo6+. The excessive water uptake facilitates excessive proton conductivity by additional growing the proton focus.
As for proton trapping, the excessive optimistic cost of the W6+ dopant results in a stronger repulsion with protons, that are additionally positively charged. This impact was confirmed by from the beginning molecular dynamics simulationswhich revealed the migration pathways of protons close to the Sc cation when transporting throughout the fabric. The repulsion signifies diminished proton trapping by the W6+ dopant, which results in the excessive proton conductivity at low and intermediate temperatures.
Taken collectively, the insights supplied by this examine might assist set up basic design rules for proton-conducting perovskites.
“The stabilization of perovskites with disordered intrinsic oxygen vacancies and full hydration enabled by doping of large donor dopant could be an effective strategy towards next-generation proton conductors,” says Yashima.
Along with PCFCs, proton conductors are additionally wanted in proton-conducting electroysis cells (PCECs), which may effectively make the most of electrical energy. Each of those applied sciences will likely be important within the close to future as we collectively attempt in direction of sustainability by novel proton conductors.
Extra info:
Kei Saito et al, Excessive proton conduction by full hydration in extremely oxygen poor perovskite, Journal of Supplies Chemistry A (2024). DOI: 10.1039/D4TA01978D
Offered by
Tokyo Institute of Technology
Quotation:
Fixing the issues of proton-conducting perovskites for next-generation gas cells (2024, Could 29)
retrieved 29 Could 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-05-problems-proton-perovskites-generation-fuel.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.