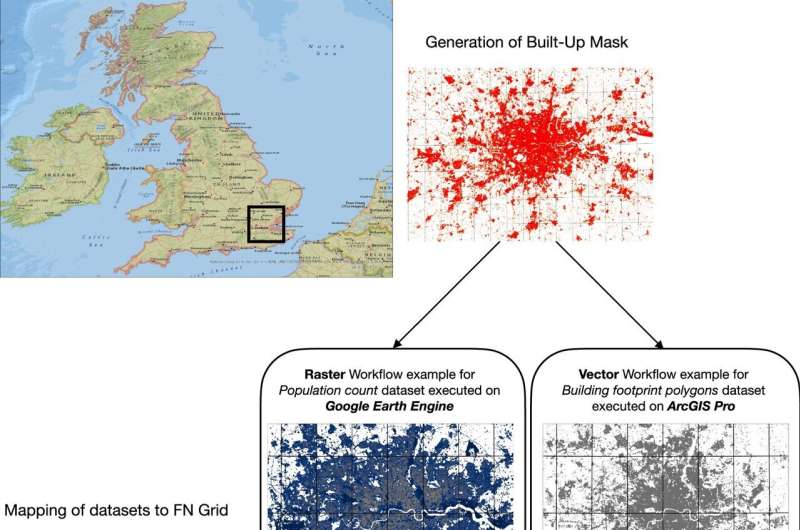
Course of move of knowledge aggregation for FN grid. Visualization of the workflow for UK with zoomed in view for London. Credit score: Scientific Knowledge (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41597-024-03378-x
A novel machine studying framework developed by IIASA researchers to estimate world rooftop space progress from 2020 to 2050 can assist in planning sustainable vitality programs, city growth, and local weather change mitigation, and has potential for important advantages in rising economies.
In 2019, buildings world wide used round 18% of yearly electrical energy generated and produced 21% of greenhouse gases launched into the environment, thereby contributing considerably to local weather change. Because the world’s inhabitants continues to develop, we are going to want extra buildings, which can in flip improve demand for each electrical energy and development supplies.
International rooftop space refers back to the complete gross floor space of all of the roofs on buildings world wide. This measurement is necessary for varied functions, resembling putting in roof mounted solar panels for clean energyplanning cities, and finding out environmental impacts.
By understanding the worldwide rooftop space and its progress within the subsequent 30 years, we are able to higher plan for sustainable vitality programs, enhance urban developmentand cut back the impacts of buildings on points resembling local weather change and biodiversity loss.
To assist with this, IIASA researchers have developed a machine learning framework that makes use of big data from about 700 million constructing footprints, world land cowl, in addition to world highway, and inhabitants data.
Their framework, which has since been published within the journal Scientific Knowledgegives estimates of rooftop space progress from 2020 to 2050 below 5 completely different future situations. The info covers roughly 3.5 million small areas worldwide.
Utilizing the framework, the researchers estimated that in 2020, the whole rooftop space globally was 0.25 million sq. kilometers, out of a complete human-made built-up floor space of 1.46 million sq. kilometers. Asia had the biggest share with 0.12 million sq. kilometers, adopted by Europe with 0.047 million, North America with 0.039 million, and Africa with 0.02 million.
By 2050, the worldwide rooftop space is anticipated to extend to between 0.3 and 0.38 million sq. kilometers, representing a 20–52% improve from 2020. Africa is projected to see the best progress, probably doubling its rooftop space.
The group’s work gives the primary high-resolution world estimate of rooftop space progress based mostly on completely different socioeconomic pathway narratives and demonstrates how massive geospatial datasets and machine studying can help sustainable growth and climate action.
The important thing takeaway is that rooftop solar power holds important potential for rising economies. With speedy rooftop space progress, these areas can leverage their manufacturing capabilities, excessive photo voltaic potential, cost-effective labor, and entrepreneurial spirit to realize sustainable development and prosperity.
“The implications of this research for policy and the public are significant. Our dataset can aid in more realistic planning of decentralized solar energy systems, thereby promoting sustainable energy solutions,” concludes lead creator Siddharth Joshi, a analysis scholar within the Built-in Evaluation and Local weather Change Analysis Group of the IIASA Power, Local weather, and Atmosphere Program.
“Estimating the potential of rooftop solar technology in achieving climate policies, especially in emerging economies, can help these policies be more effective and affordable, in line with the Sustainable Development Goals for clean energy, sustainable cities, climate action, and life on land.”
Joshi began work on the conceptualization, growth, and evaluation of the framework whereas collaborating within the 2021 IIASA Younger Scientists Summer season Program. He acquired the Mikhalevich Award for his work on this regard.
The complete dataset is available online.
Extra data:
Siddharth Joshi et al, International high-resolution progress projections dataset for rooftop space according to the shared socioeconomic pathways, 2020–2050, Scientific Knowledge (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41597-024-03378-x
Offered by
Worldwide Institute for Utilized Techniques Evaluation (IIASA)
Quotation:
Machine studying framework maps world rooftop progress for sustainable vitality and concrete planning (2024, July 16)
retrieved 17 July 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-07-machine-framework-global-rooftop-growth.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.